C++笔记之环形队列
code review!
文章目录
- C++笔记之环形队列
- 1.概念I——摘自 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/HUn9TF09RZ-UJKYPR5ZXhA
- 2.概念II——摘自 http://t.csdnimg.cn/72bng
- 3.概念III—— 摘自https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/9Ga502p1DLcc6o75JBQlDg
- 4.概念IV—— 摘自https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/pJaIlUrZoEmLzWJfP2Nyyw
- 5.一种更好的计算队尾指针的方法—— 摘自https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/g2WBerFa0MaAsounduG43A
- 6.环形队列中读写使用索引和指针的比较
- 7.例:使用数组实现一个简单的环形队列
- 8.例:使用vector实现一个简单的环形队列
- 9.C++使用环形队列实现一个完整的生产者-消费者简单例程
1.概念I——摘自 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/HUn9TF09RZ-UJKYPR5ZXhA
-
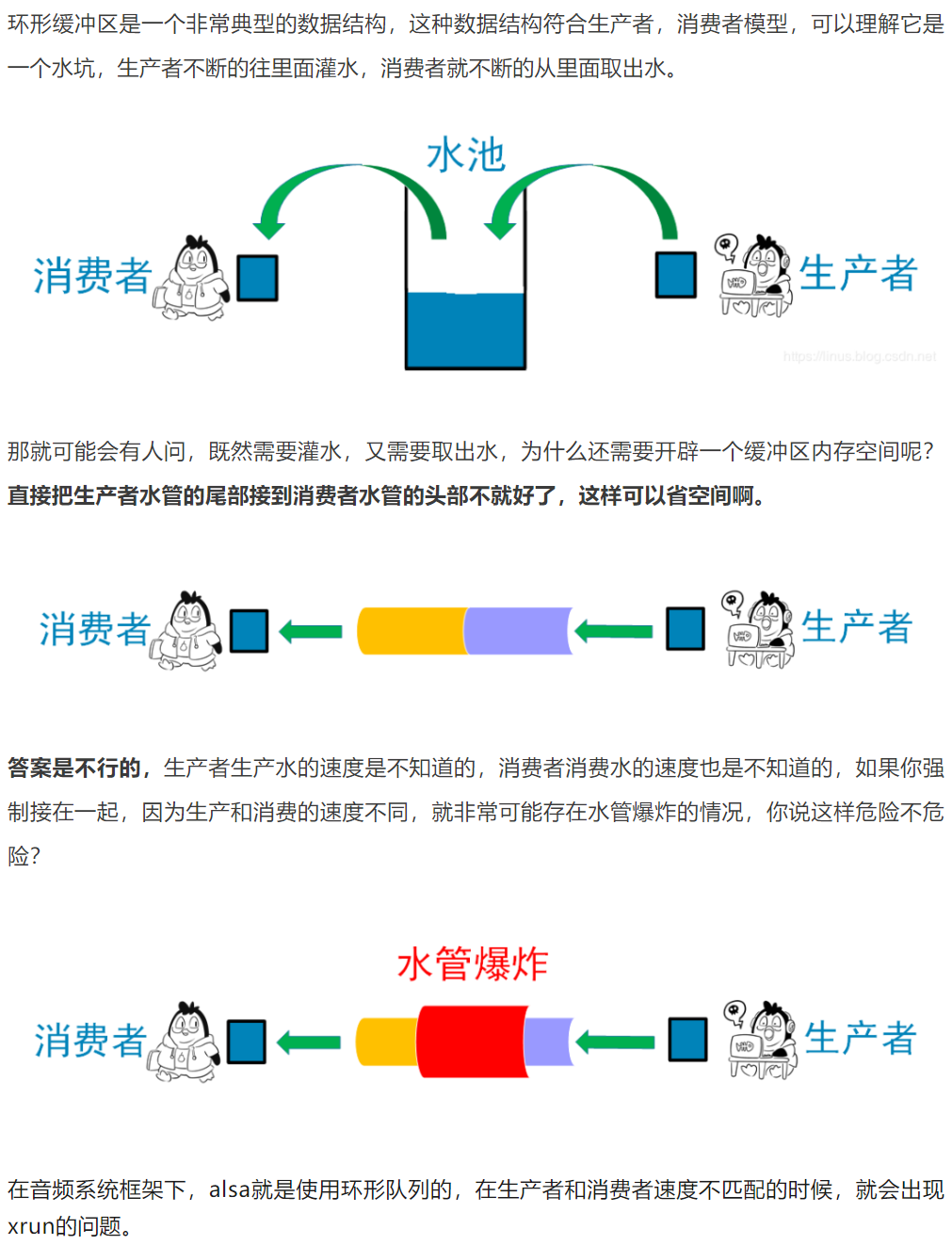
1、数组构造环形缓冲区
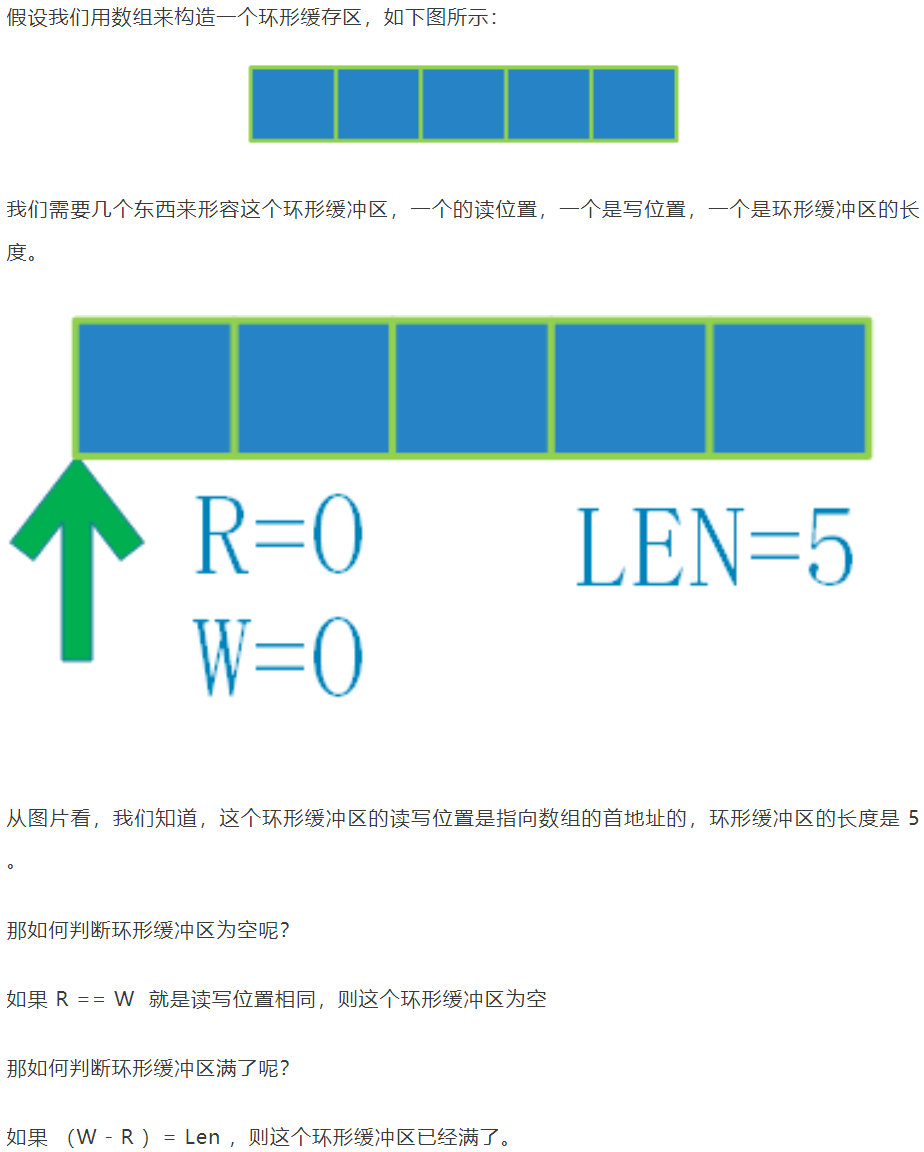
-
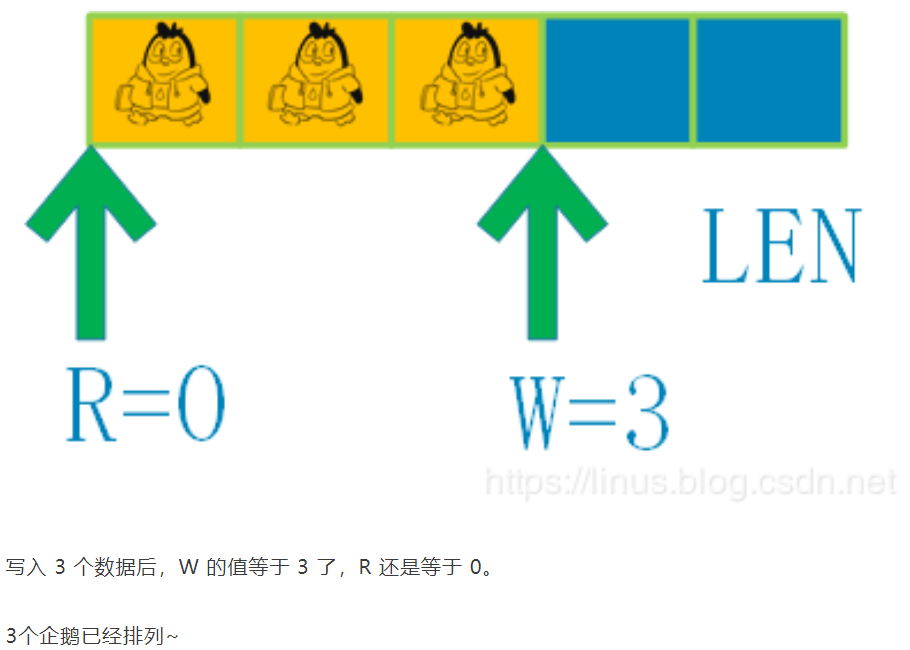
2、向环形缓冲区写入3个数据
-
3、从环形缓冲区读取2个数据
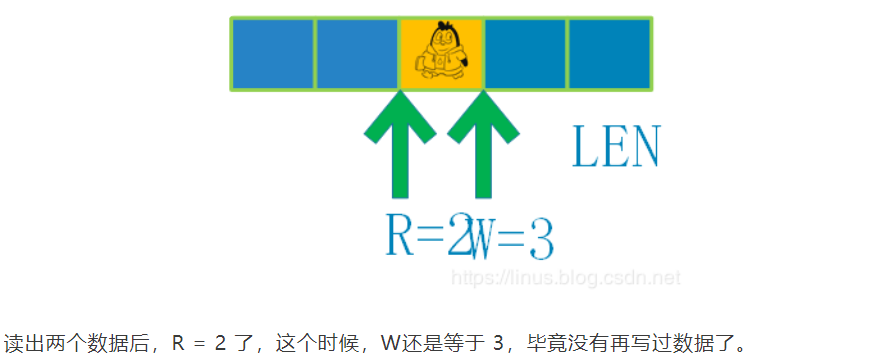
-
4、再写入3个数据
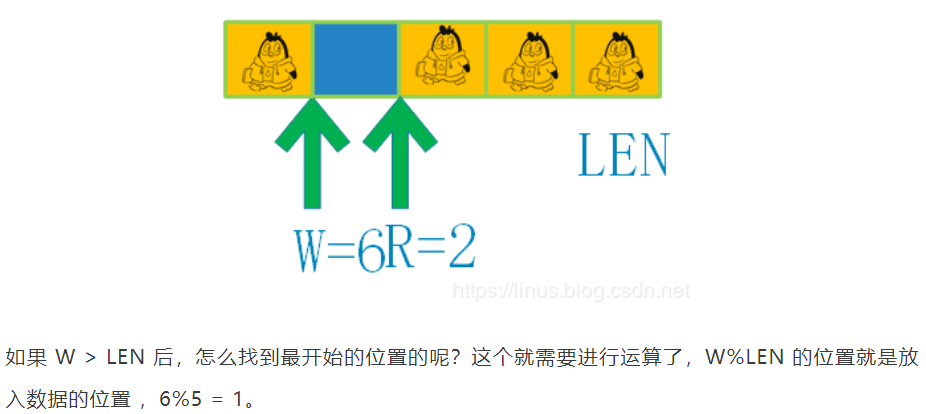
-
5、再写入1个数据
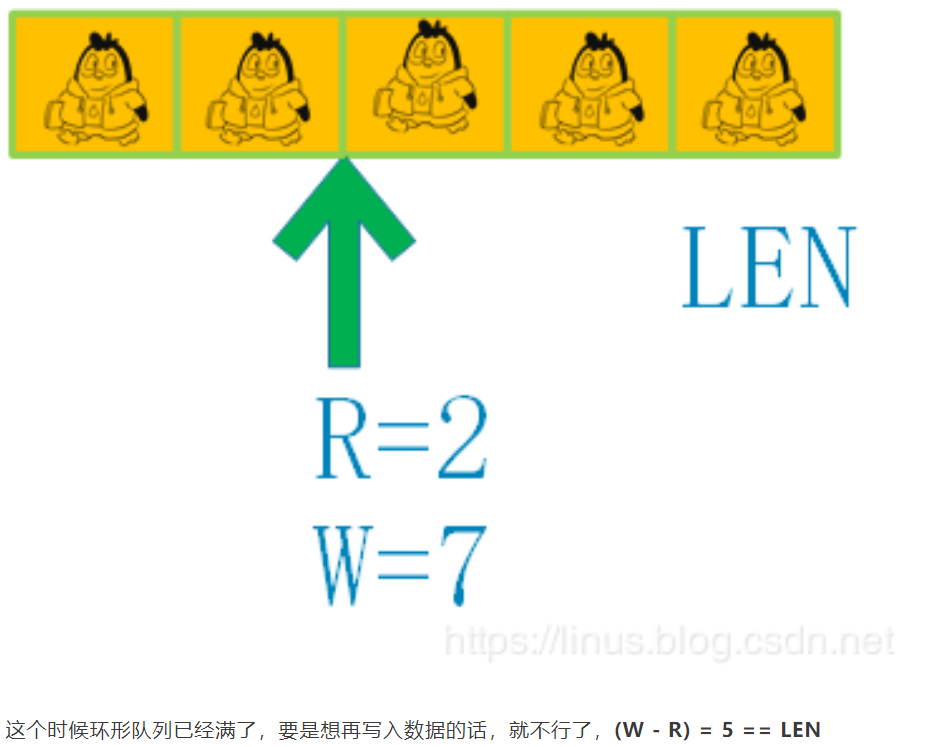
-
6、代码实现
/* 实现的最简单的ringbuff 有更多提升空间,可以留言说明 */
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#define LEN 10
/*环形队列结构体*/
typedef struct ring_buff{
int array[LEN];
int W;
int R;
}*ring;
/*环形队列初始化*/
struct ring_buff * fifo_init(void)
{
struct ring_buff * p = NULL;
p = (struct ring_buff *)malloc(sizeof(struct ring_buff));
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("fifo_init malloc error\n");
return NULL;
}
p->W = 0;
p->R = 0;
return p;
}
/*判断环形队列是否已经满了*/
int get_ring_buff_fullstate(struct ring_buff * p_ring_buff)
{
/*如果写位置减去读位置等于队列长度,就说明这个环形队列已经满*/
if((p_ring_buff->W - p_ring_buff->R) == LEN)
{
return (1);
}
else
{
return (0);
}
}
/*判断环形队列为空*/
int get_ring_buff_emptystate(struct ring_buff * p_ring_buff)
{
/*如果写位置和读的位置相等,就说明这个环形队列为空*/
if(p_ring_buff->W == p_ring_buff->R)
{
return (1);
}
else
{
return (0);
}
}
/*插入数据*/
int ring_buff_insert(struct ring_buff * p_ring_buff,int data)
{
if(p_ring_buff == NULL)
{
printf("p null\n");
return (-1);
}
if(get_ring_buff_fullstate(p_ring_buff) == 1)
{
printf("buff is full\n");
return (-2);
}
p_ring_buff->array[p_ring_buff->W%LEN] = data;
p_ring_buff->W ++;
//printf("inset:%d %d\n",data,p_ring_buff->W);
return (0);
}
/*读取环形队列数据*/
int ring_buff_get(struct ring_buff * p_ring_buff)
{
int data = 0;
if(p_ring_buff == NULL)
{
printf("p null\n");
return (-1);
}
if(get_ring_buff_emptystate(p_ring_buff) == 1)
{
printf("buff is empty\n");
return (-2);
}
data = p_ring_buff->array[p_ring_buff->R%LEN];
p_ring_buff->R++;
return data;
}
/*销毁*/
int ring_buff_destory(struct ring_buff * p_ring_buff)
{
if(p_ring_buff == NULL)
{
printf("p null\n");
return (-1);
}
free(p_ring_buff);
return (0);
}
int main()
{
int i = 0;
/*定义一个环形缓冲区*/
ring pt_ring_buff = fifo_init();
/*向环形缓冲区中写入数据*/
for(i = 0;i<10;i++)
{
ring_buff_insert(pt_ring_buff,i);
}
/*从环形缓冲区中读出数据*/
for(i = 0;i<10;i++)
{
printf("%d ",ring_buff_get(pt_ring_buff));
}
/*销毁一个环形缓冲区*/
ring_buff_destory(pt_ring_buff);
return (1);
}
运行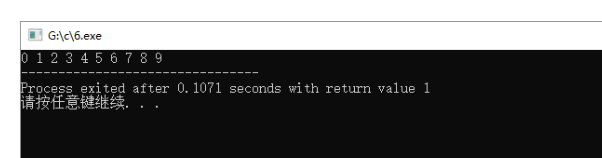
2.概念II——摘自 http://t.csdnimg.cn/72bng

3.概念III—— 摘自https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/9Ga502p1DLcc6o75JBQlDg
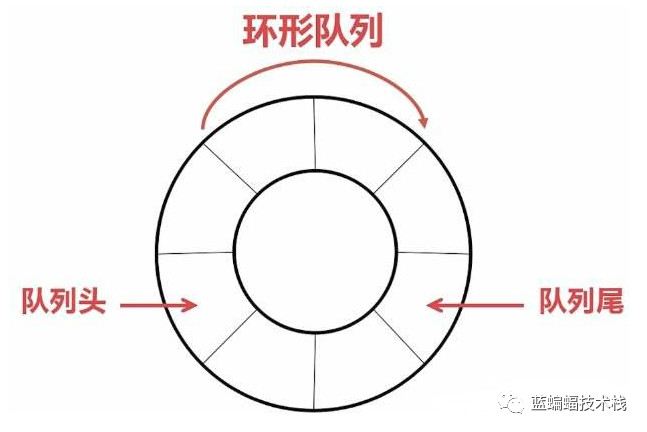
-
实现环形队列图示过程
-
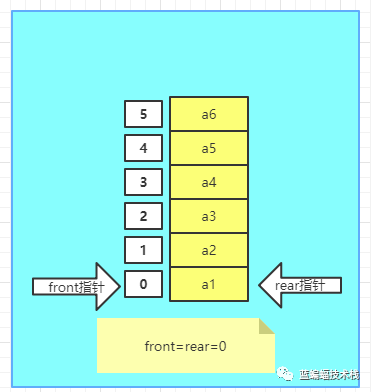
- 初始化一个数组大小为6的环形队列, 头指针front=0, 尾指针rear=0, 刚好front=rear =0的状态,表示环形队列为空.
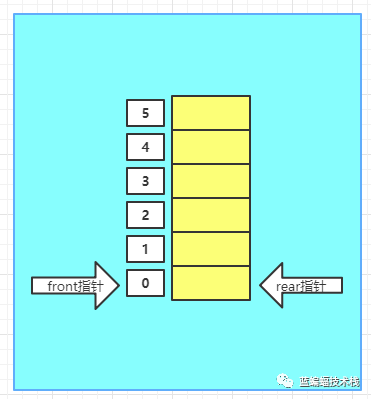
- 初始化一个数组大小为6的环形队列, 头指针front=0, 尾指针rear=0, 刚好front=rear =0的状态,表示环形队列为空.
-
- 向环形队列里插入1个元素,则rear指针移动一格,front=0,rear=1
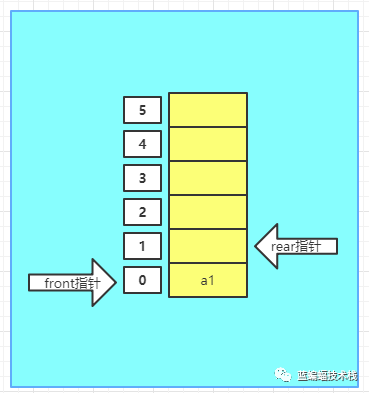
- 向环形队列里插入1个元素,则rear指针移动一格,front=0,rear=1
-
3.继续添加a2,a3,a4,a5元素,rear指针指到末尾处,front=0, reat=5
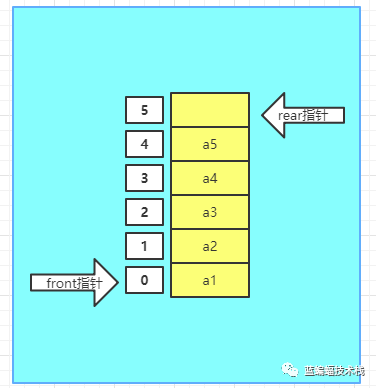
-
4.如果再继续添加a6元素,则rear=6,大于数组大小,发生数组溢出.
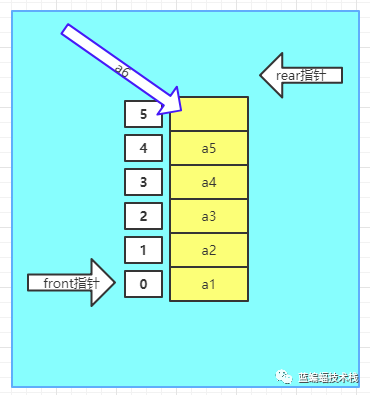
-
5.如上图所示添加a6时,rear指针发生溢出.我们使用一个小技巧,当rear=6时与数组大小6进行取模, (rear+1) % maxLen,让rear指针回到开始处rear=0,问题来了,我们无法判断数组是否满?因为初始化时front=rear=0, 现在数组满也是front=rear=0
-
6.解决以上问题有三种办法,我们采用第3种方法实现.

使用第3种方法: 即当(rear+1) % maxLen == front时,判断环形数组满,则无法添加元素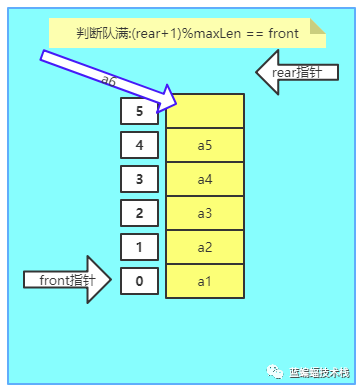
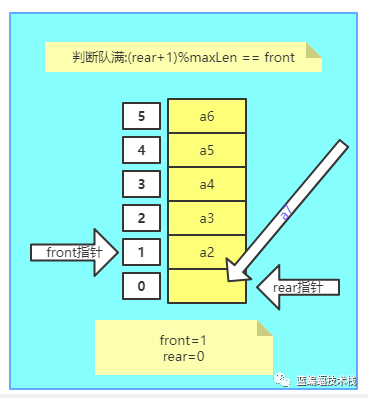
4.概念IV—— 摘自https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/pJaIlUrZoEmLzWJfP2Nyyw
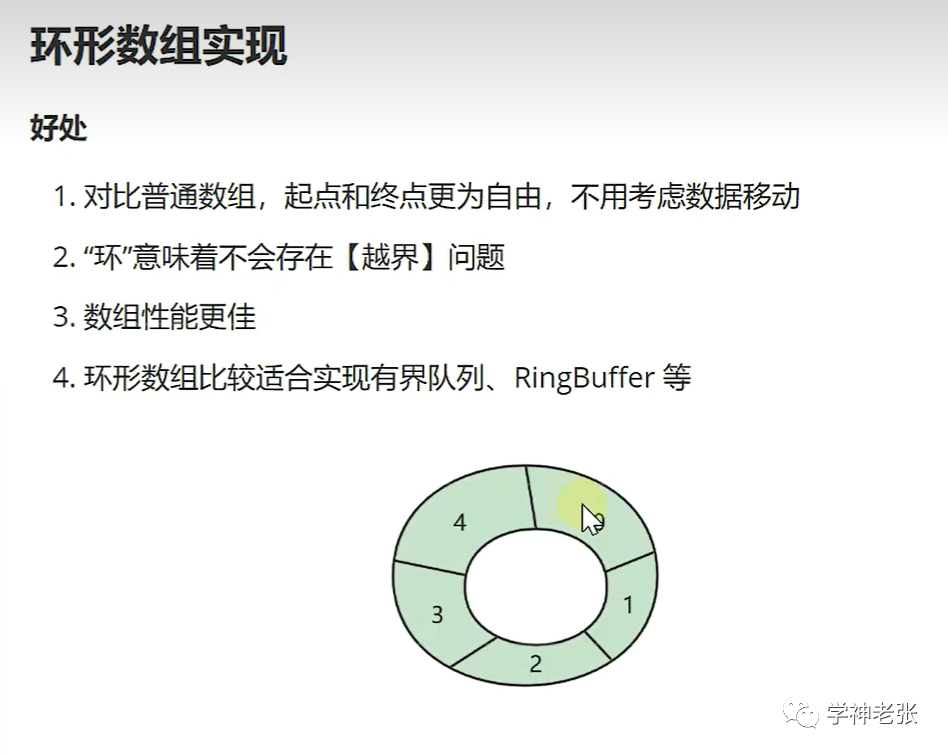
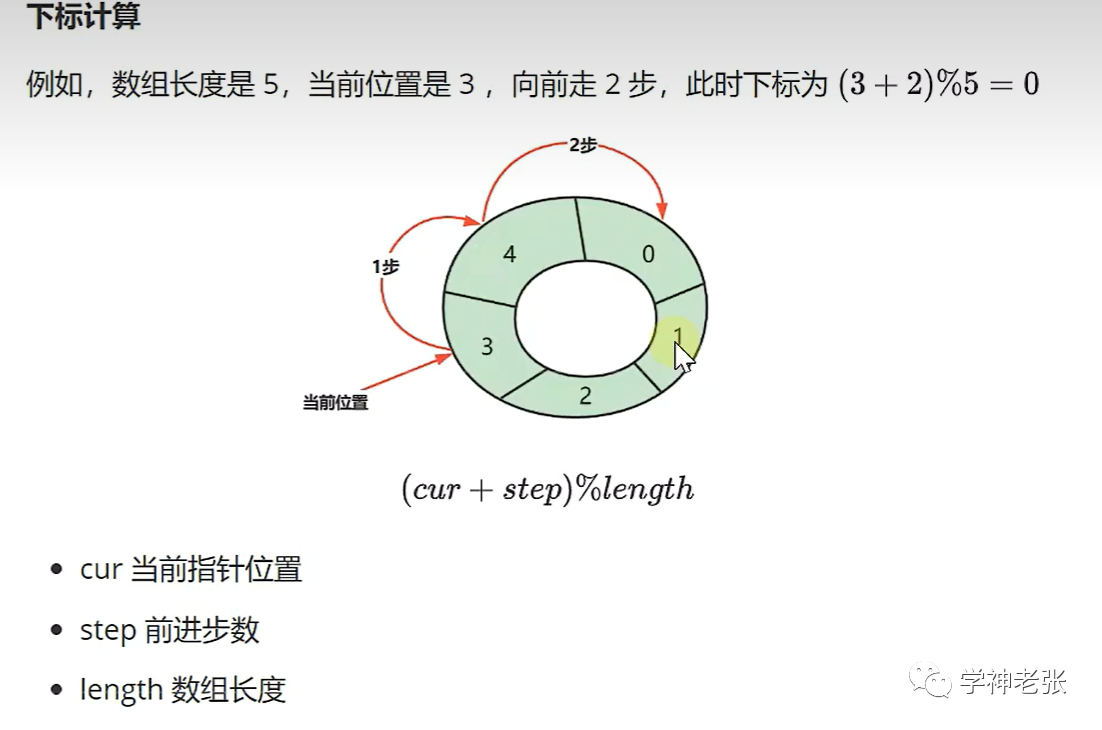
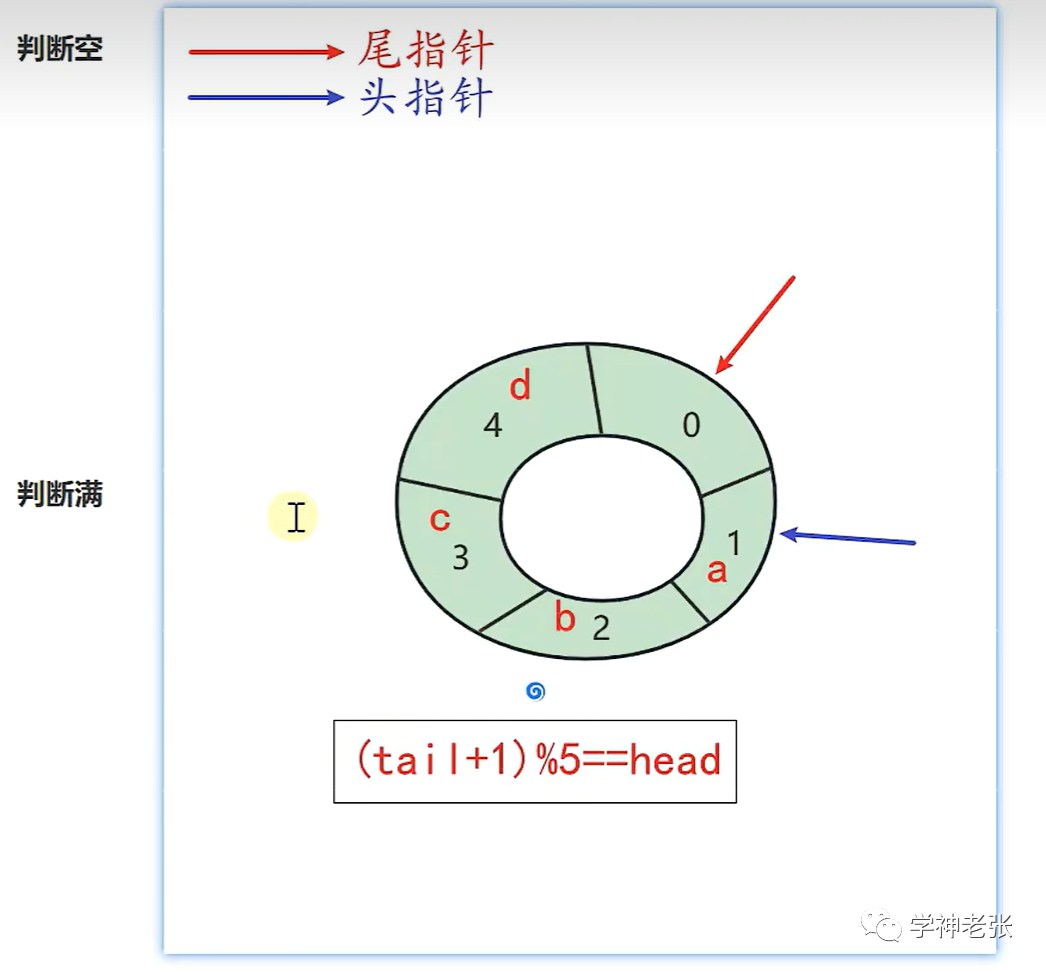
头指针和尾指针指向同一个位置代表当前队列为空,当前环形队列不能将数据插满,如果插满则无法判断队列为空的情况。所以最后一个位置要空出来,不插入值。判定队列满的情况则是用尾指针的下一个指针指向头则说明当前环形队列已满。
5.一种更好的计算队尾指针的方法—— 摘自https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/g2WBerFa0MaAsounduG43A

6.环形队列中读写使用索引和指针的比较
在C++中实现环形队列时,可以使用索引或指针来表示读和写的位置,具体取决于你的实现方式和个人偏好。以下是两种常见的方法:
- 使用索引:
在这种方法中,你可以使用两个索引来表示队列的读和写位置。一个索引表示队列的头部,另一个表示队列的尾部。当元素被入队时,尾部索引递增;当元素被出队时,头部索引递增。当索引到达队列的末尾时,可以通过取模运算将其重置为队列的开头,以实现环形队列的特性。
int queue[MAX_SIZE]; // 假设队列的最大大小是MAX_SIZE
int front = 0; // 头部索引
int rear = 0; // 尾部索引
// 入队操作
void enqueue(int item) {
if ((rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE == front) {
// 队列已满
cout << "队列已满,无法入队" << endl;
return;
}
queue[rear] = item;
rear = (rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
}
// 出队操作
int dequeue() {
if (front == rear) {
// 队列为空
cout << "队列为空,无法出队" << endl;
return -1; // 返回一个特定的错误值或抛出异常
}
int item = queue[front];
front = (front + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
return item;
}
- 使用指针:
另一种方法是使用指针来表示队列的读和写位置。你可以使用两个指针,一个指向队列的头部,另一个指向队列的尾部。入队和出队操作会移动这些指针,并确保它们在环形队列中正确移动。
int queue[MAX_SIZE]; // 假设队列的最大大小是MAX_SIZE
int *front = queue; // 头部指针
int *rear = queue; // 尾部指针
// 入队操作
void enqueue(int item) {
if ((rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE == front) {
// 队列已满
cout << "队列已满,无法入队" << endl;
return;
}
*rear = item;
rear = (rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
}
// 出队操作
int dequeue() {
if (front == rear) {
// 队列为空
cout << "队列为空,无法出队" << endl;
return -1; // 返回一个特定的错误值或抛出异常
}
int item = *front;
front = (front + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
return item;
}
横向排版对比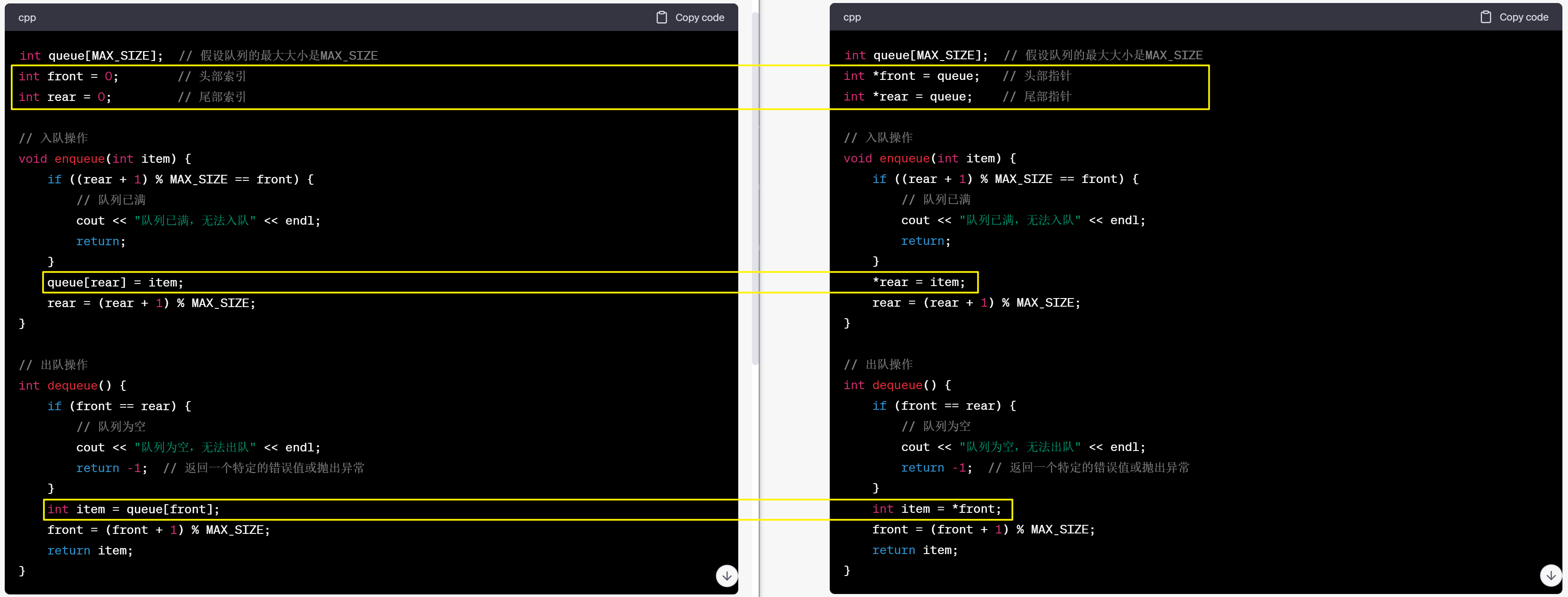
无论你选择使用索引还是指针,都可以实现一个有效的环形队列。选择哪种方式取决于你的偏好和实际需求。指针的方法在某些情况下可能更直观,因为你可以像操作普通数组一样操作指针,而无需进行索引运算。但索引方法也是常见的,因为它们更容易理解和实现。
7.例:使用数组实现一个简单的环形队列
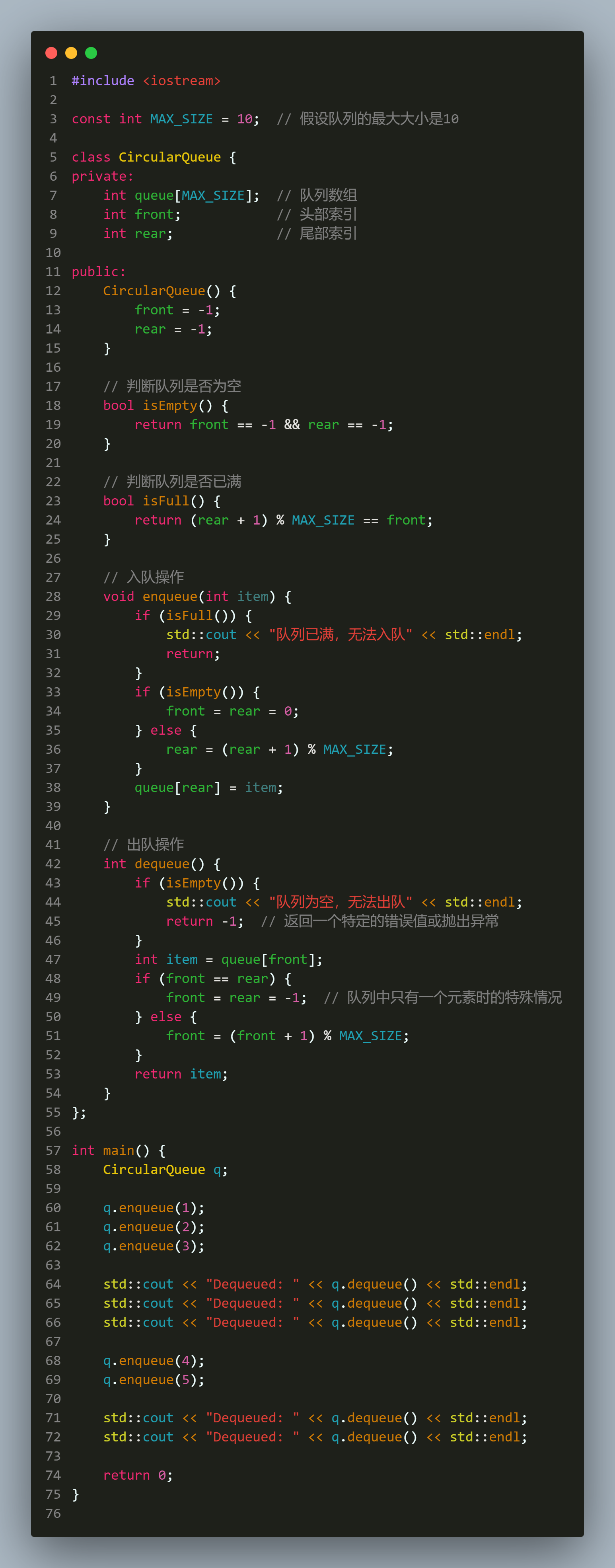
代码
#include <iostream>
const int MAX_SIZE = 10; // 假设队列的最大大小是10
class CircularQueue {
private:
int queue[MAX_SIZE]; // 队列数组
int front; // 头部索引
int rear; // 尾部索引
public:
CircularQueue() {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
// 判断队列是否为空
bool isEmpty() {
return front == -1 && rear == -1;
}
// 判断队列是否已满
bool isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE == front;
}
// 入队操作
void enqueue(int item) {
if (isFull()) {
std::cout << "队列已满,无法入队" << std::endl;
return;
}
if (isEmpty()) {
front = rear = 0;
} else {
rear = (rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
}
queue[rear] = item;
}
// 出队操作
int dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
std::cout << "队列为空,无法出队" << std::endl;
return -1; // 返回一个特定的错误值或抛出异常
}
int item = queue[front];
if (front == rear) {
front = rear = -1; // 队列中只有一个元素时的特殊情况
} else {
front = (front + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
}
return item;
}
};
int main() {
CircularQueue q;
q.enqueue(1);
q.enqueue(2);
q.enqueue(3);
std::cout << "Dequeued: " << q.dequeue() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Dequeued: " << q.dequeue() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Dequeued: " << q.dequeue() << std::endl;
q.enqueue(4);
q.enqueue(5);
std::cout << "Dequeued: " << q.dequeue() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Dequeued: " << q.dequeue() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
运行
Dequeued: 1
Dequeued: 2
Dequeued: 3
Dequeued: 4
Dequeued: 5文章来源:https://uudwc.com/A/4rnz3
8.例:使用vector实现一个简单的环形队列
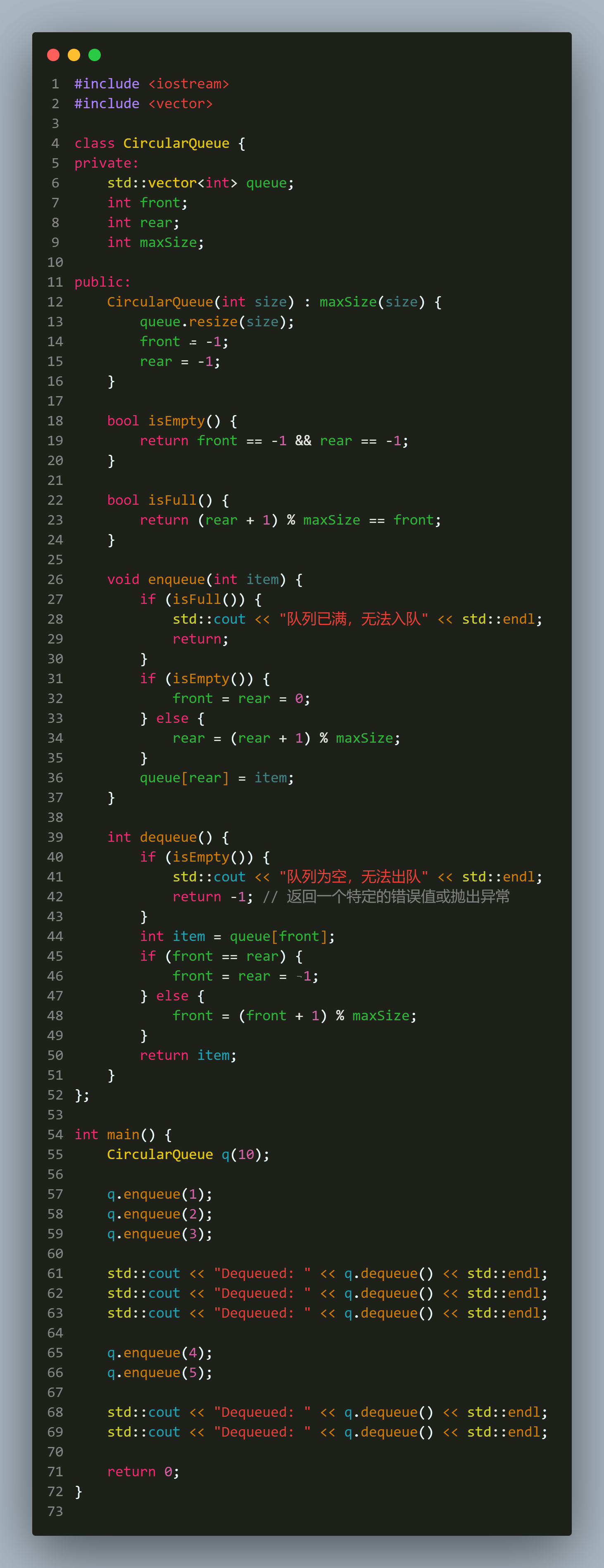
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
class CircularQueue {
private:
std::vector<int> queue;
int front;
int rear;
int maxSize;
public:
CircularQueue(int size) : maxSize(size) {
queue.resize(size);
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
bool isEmpty() {
return front == -1 && rear == -1;
}
bool isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % maxSize == front;
}
void enqueue(int item) {
if (isFull()) {
std::cout << "队列已满,无法入队" << std::endl;
return;
}
if (isEmpty()) {
front = rear = 0;
} else {
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;
}
queue[rear] = item;
}
int dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
std::cout << "队列为空,无法出队" << std::endl;
return -1; // 返回一个特定的错误值或抛出异常
}
int item = queue[front];
if (front == rear) {
front = rear = -1;
} else {
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
}
return item;
}
};
int main() {
CircularQueue q(10);
q.enqueue(1);
q.enqueue(2);
q.enqueue(3);
std::cout << "Dequeued: " << q.dequeue() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Dequeued: " << q.dequeue() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Dequeued: " << q.dequeue() << std::endl;
q.enqueue(4);
q.enqueue(5);
std::cout << "Dequeued: " << q.dequeue() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Dequeued: " << q.dequeue() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
运行
Dequeued: 1
Dequeued: 2
Dequeued: 3
Dequeued: 4
Dequeued: 5
9.C++使用环形队列实现一个完整的生产者-消费者简单例程
运行
代码文章来源地址https://uudwc.com/A/4rnz3
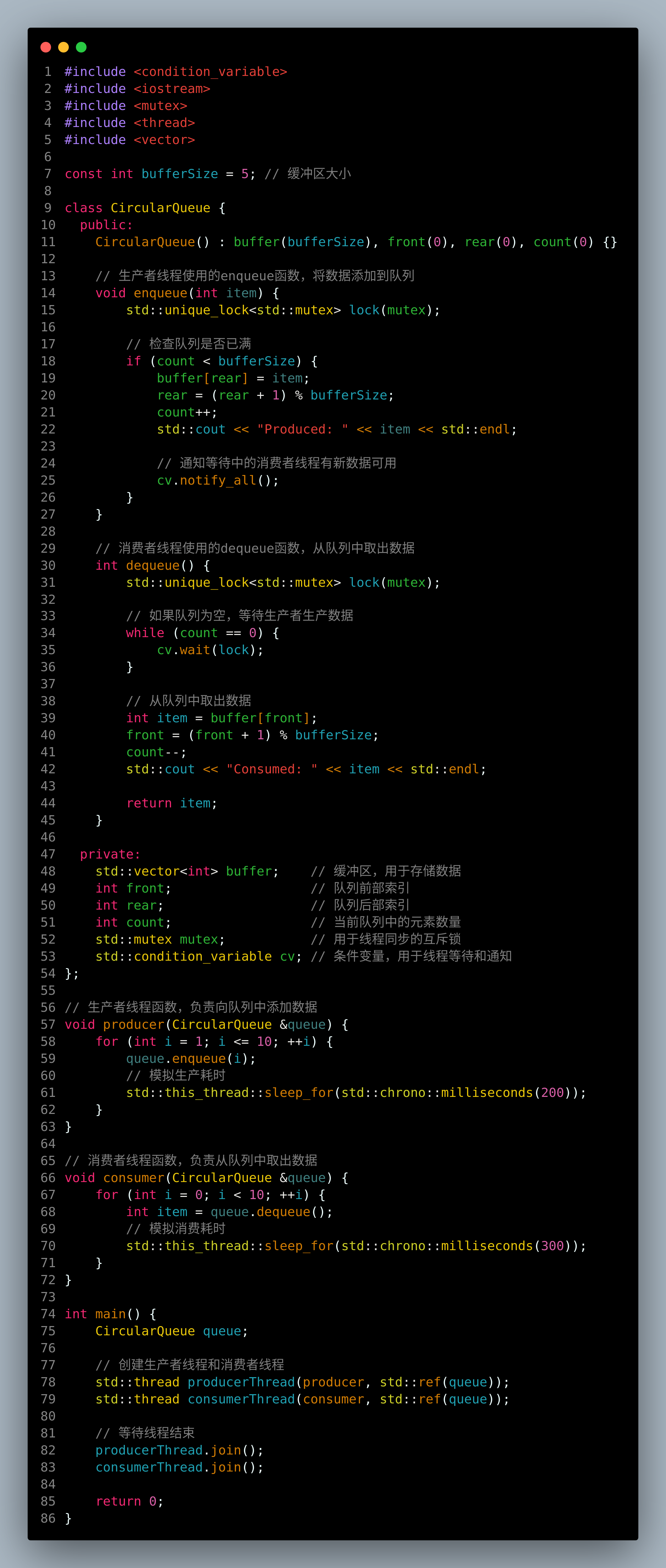
#include <condition_variable>
#include <iostream>
#include <mutex>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
const int bufferSize = 5; // 缓冲区大小
class CircularQueue {
public:
CircularQueue() : buffer(bufferSize), front(0), rear(0), count(0) {}
// 生产者线程使用的enqueue函数,将数据添加到队列
void enqueue(int item) {
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex);
// 检查队列是否已满
if (count < bufferSize) {
buffer[rear] = item;
rear = (rear + 1) % bufferSize;
count++;
std::cout << "Produced: " << item << std::endl;
// 通知等待中的消费者线程有新数据可用
cv.notify_all();
}
}
// 消费者线程使用的dequeue函数,从队列中取出数据
int dequeue() {
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex);
// 如果队列为空,等待生产者生产数据
while (count == 0) {
cv.wait(lock);
}
// 从队列中取出数据
int item = buffer[front];
front = (front + 1) % bufferSize;
count--;
std::cout << "Consumed: " << item << std::endl;
return item;
}
private:
std::vector<int> buffer; // 缓冲区,用于存储数据
int front; // 队列前部索引
int rear; // 队列后部索引
int count; // 当前队列中的元素数量
std::mutex mutex; // 用于线程同步的互斥锁
std::condition_variable cv; // 条件变量,用于线程等待和通知
};
// 生产者线程函数,负责向队列中添加数据
void producer(CircularQueue &queue) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i) {
queue.enqueue(i);
// 模拟生产耗时
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(200));
}
}
// 消费者线程函数,负责从队列中取出数据
void consumer(CircularQueue &queue) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
int item = queue.dequeue();
// 模拟消费耗时
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(300));
}
}
int main() {
CircularQueue queue;
// 创建生产者线程和消费者线程
std::thread producerThread(producer, std::ref(queue));
std::thread consumerThread(consumer, std::ref(queue));
// 等待线程结束
producerThread.join();
consumerThread.join();
return 0;
}