SpringBoot 利用 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 批量插入万条数据
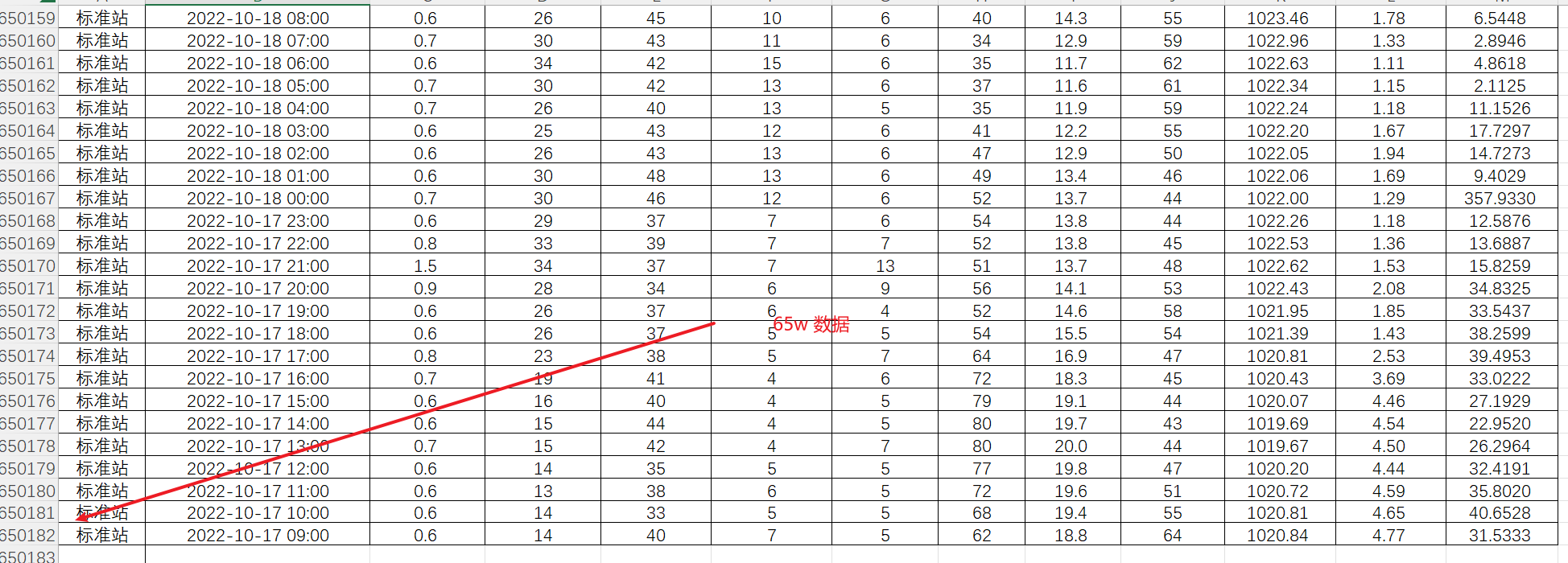
在批处理插入数据时,如果在单线程环境下是非常耗时的,本篇文章将采用单线程和多线程进行对比,利用 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 进行多线程批处理插入65w数据,然后和单线程进行对比,最终得到性能优化。

yml 文件配置
# 异步线程池配置
thread:
pool:
corePoolSize: 8 # 核心线程数
maxPoolSize: 20 # 设置最大线程数
keepAliveSeconds: 300 # 设置线程活跃时间
queueCapacity: 100 # 设置队列容量
prefixName: async-service- # 线程名称前缀
spring 容器注入线程池 bean 对象
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "thread.pool")
public class ThreadPoolConfig {
/**
* 核心线程数
*/
private Integer corePoolSize;
/**
* 设置最大线程数
*/
private Integer maxPoolSize;
/**
* 设置线程活跃时间
*/
private Integer keepAliveSeconds;
/**
* 设置队列容量
*/
private Integer queueCapacity;
/**
* 线程名称前缀
*/
private String prefixName;
}
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
@Slf4j
public class ThreadPoolExecutorConfig {
private ThreadPoolConfig threadPoolConfig;
public ThreadPoolExecutorConfig(ThreadPoolConfig threadPoolConfig) {
this.threadPoolConfig = threadPoolConfig;
}
@Bean(name = "asyncServiceExecutor")
public Executor asyncServiceExecutor() {
log.info("start asyncServiceExecutor");
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(threadPoolConfig.getCorePoolSize());
executor.setMaxPoolSize(threadPoolConfig.getMaxPoolSize());
executor.setQueueCapacity(threadPoolConfig.getQueueCapacity());
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(threadPoolConfig.getKeepAliveSeconds());
executor.setThreadNamePrefix(threadPoolConfig.getPrefixName());
// 拒绝策略
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
// 初始化
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
创建异步线程业务类
@Service
@Slf4j
public class AsyncServiceImpl implements AsyncService {
@Override
@Async("asyncServiceExecutor")
public void executeAsync(List<StandardStation> list, StandardStationService standardStationService, CountDownLatch countDownLatch) {
try {
log.info("start executeAsync");
// 异步线程需要做的事情
standardStationService.saveBatch(list);
log.info("end executeAsync");
} finally {
// 无论上面程序是否异常必须执行 countDown,否则 await 无法释放
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}
}
创建单线程批量插入具体业务方法
/**
* 单线程插入 650000 条数据
*/
@Test
public void testSingleThread() {
// 10000 条数据
List<StandardStation> standardStationList = list.stream().map(info -> {
StandardStation standardStation = new StandardStation();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(info, standardStation);
return standardStation;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 单线程 每 100 条数据插入一次
List<List<StandardStation>> lists = Lists.partition(standardStationList, 100);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
lists.forEach(listSub -> standardStationService.saveBatch(listSub));
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("共耗时:{} 秒", (endTime - startTime) / 1000);
}
结果:

创建多线程批量插入具体业务方法
/**
* 多线程插入 650000 条数据
*/
@Test
public void testMultiThread() {
// 10000 条数据
List<StandardStation> standardStationList = list.stream().map(info -> {
StandardStation standardStation = new StandardStation();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(info, standardStation);
return standardStation;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 每 100 条数据插入开一个线程
List<List<StandardStation>> lists = Lists.partition(standardStationList, 100);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(lists.size());
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
lists.forEach(listSub -> asyncService.executeAsync(listSub, standardStationService, countDownLatch));
try {
// 保证之前的所有的线程都执行完成,才会走下面的
countDownLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("阻塞异常:" + e.getMessage());
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("共耗时:{} 秒", (endTime - startTime) / 1000);
}
结果:
 文章来源:https://uudwc.com/A/Lmzzo
文章来源:https://uudwc.com/A/Lmzzo
从上述的结果可以看出,使用多线程后,批处理插入大量数据的耗时大大减少,由此可见多线程的好处。文章来源地址https://uudwc.com/A/Lmzzo