java虚拟线程介绍
虚拟线程是 Java 19 的 预览特性,估计会在Java 21被纳入 JDK 的正式版本中,会在2023年9月发布,目前springboot 3 已经提供了对虚拟线程的支持。
虚拟线程和平台线程主要区别在于,虚拟线程在运行周期内不依赖操作系统线程:它们与硬件脱钩,因此被称为 “虚拟”。这种解耦是由 JVM 提供的抽象层赋予的。
虚拟线程的运行成本远低于平台线程。消耗的内存要少得多。这就是为什么可以创建数百万个虚拟线程而不会出现内存不足的问题,而标准平台(或内核)线程只能创建数百个。
从理论上讲,这赋予了开发人员一种超级能力:无需依赖异步代码即可实现高性能的应用程序。
预计在不久的未来,常见的开源框架(Tomcat、Spring、Netty)都会基于虚拟线程推出新版本。
环境准备
java 20:下载地址:OpenJDK JDK 20.0.2 GA Release
idea社区版2023.2版本,目前最高支持到java 20,下载地址:下载 IntelliJ IDEA – 领先的 Java 和 Kotlin IDE
新建springboot3项目
https://start.spring.io/
 在idea打开项目,最终项目文件如下图。修改项目设置:
在idea打开项目,最终项目文件如下图。修改项目设置:
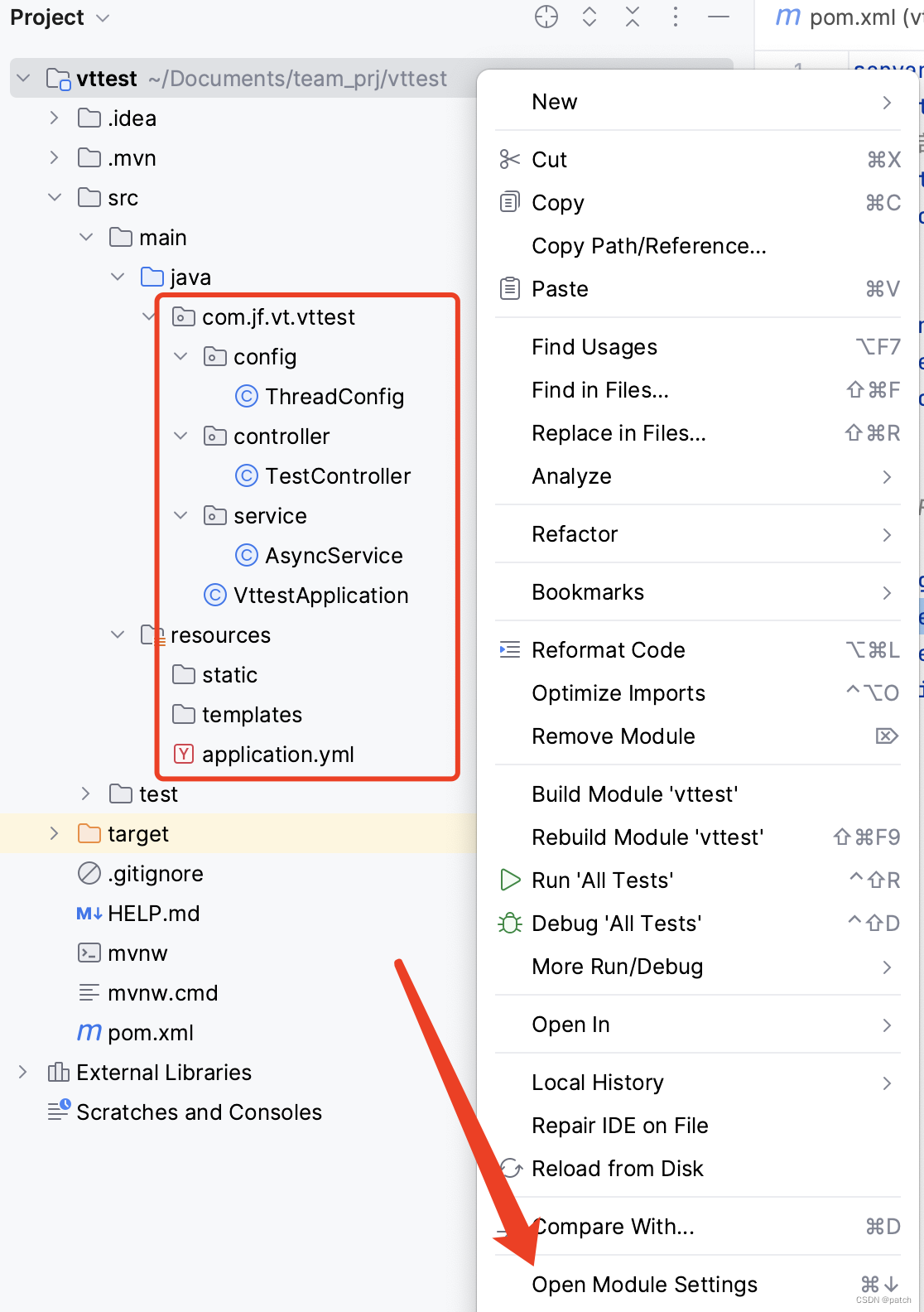

 项目文件
项目文件
POM文件:修改后一定要执行一次:Maven--reload project
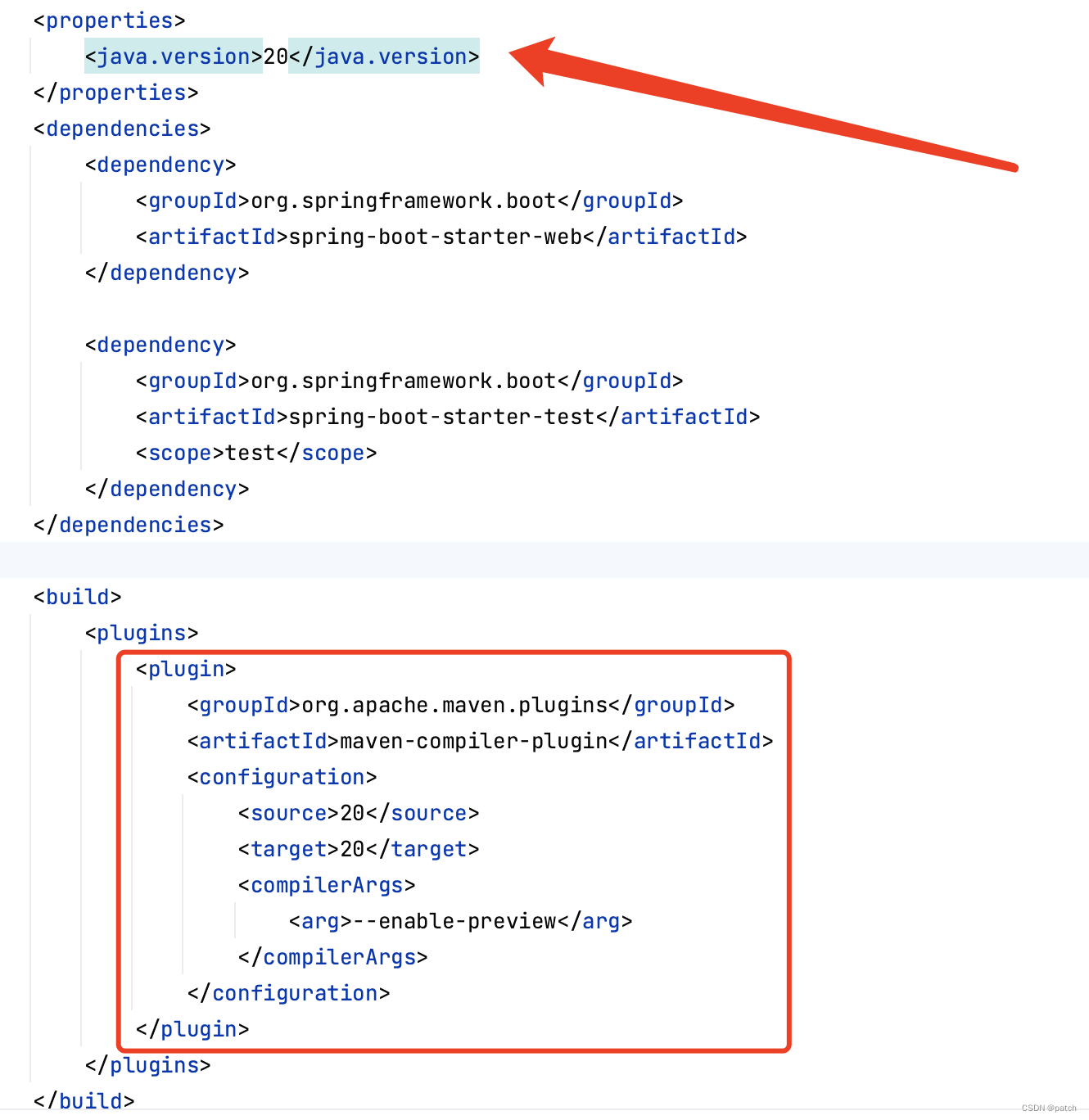
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>20</source>
<target>20</target>
<compilerArgs>
<arg>--enable-preview</arg>
</compilerArgs>
</configuration>
</plugin>springboot启动文件
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync
public class VttestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(VttestApplication.class, args);
}
}ThreadConfig.java
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.thread-executor", havingValue = "virtual")
public class ThreadConfig {
@Bean
public AsyncTaskExecutor applicationTaskExecutor() {
return new TaskExecutorAdapter(Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor());
}
@Bean
public TomcatProtocolHandlerCustomizer<?> protocolHandlerCustomizer() {
return protocolHandler -> {
protocolHandler.setExecutor(Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor());
};
}
}AsyncService.java
@Service
public class AsyncService {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(AsyncService.class);
/**
*
* @param countDownLatch 用于测试
*/
@Async
public void doSomething(CountDownLatch countDownLatch) {
// log.info(Thread.currentThread());
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
ie.printStackTrace();
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}TestController.java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(TestController.class);
@Autowired
AsyncService asyncService;
@GetMapping("/vt")
public String vt() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int n = 10000;
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
asyncService.doSomething(countDownLatch);
}
try {
countDownLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
ie.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("耗时:" + (end - start) + "ms");
return "OK";
}
@GetMapping("/ds")
public void doSomething() throws InterruptedException {
// log.info("hey, I'm doing something");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}application.yml
server:
port: 8092
#开启优雅停机,默认immediate是立即关机
shutdown: graceful
tomcat.threads.max: ${TOMCAT_THREAD_NUM:800}
logging:
level:
com:
demo:
springboottest: DEBUG
# ROOT: debug
spring:
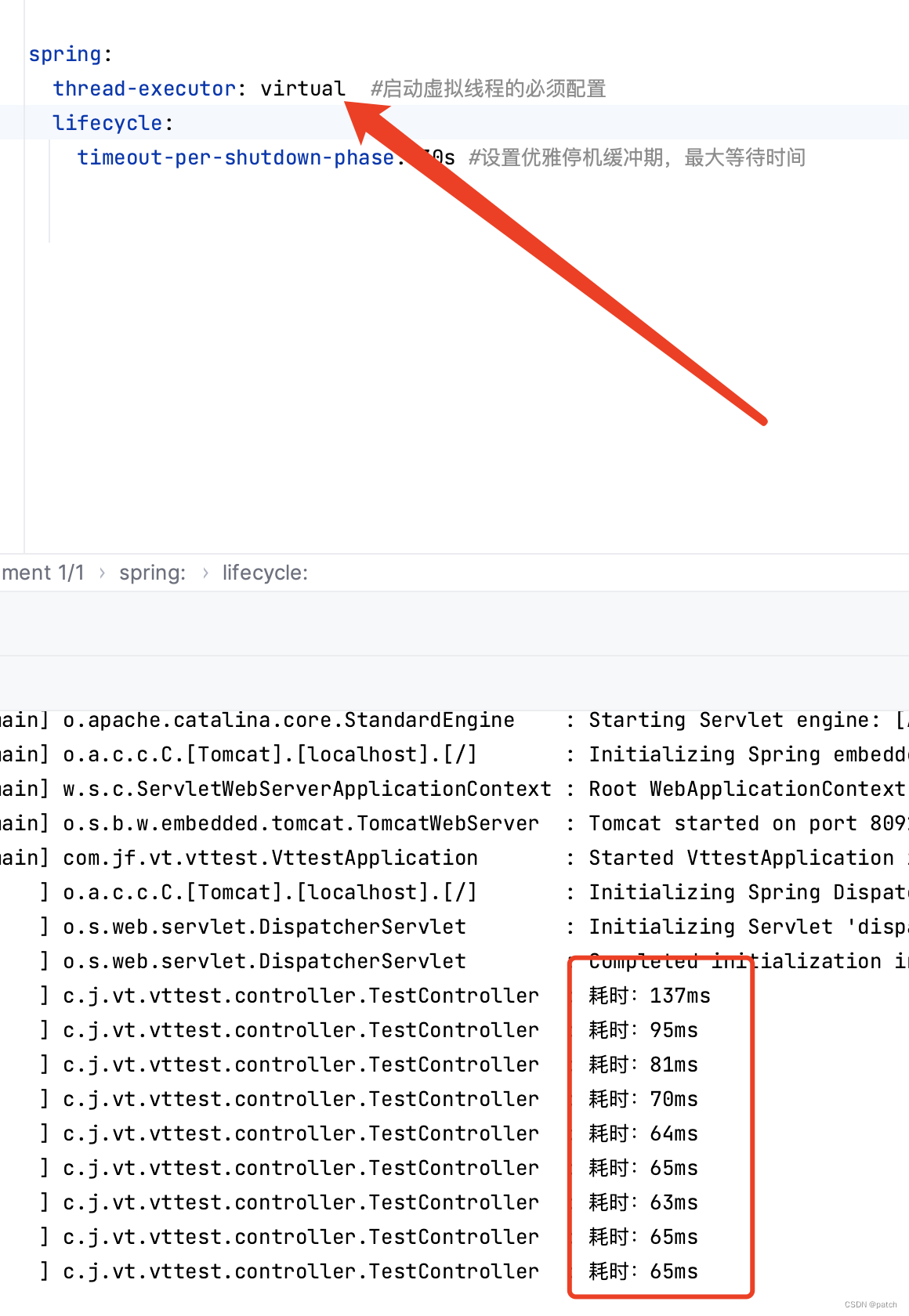
thread-executor: virtual #启动虚拟线程的必须配置
lifecycle:
timeout-per-shutdown-phase: 30s #设置优雅停机缓冲期,最大等待时间
关键是:thread-executor: virtual #启动虚拟线程的必须配置
注释掉该行则使用普通线程,后面对比虚拟线程与普通线程性能时,可通过注释该行切换到普通线程
运行项目

通过接口 http://127.0.0.1:8092/test/vt 验证两种线程执行效率
虚拟线程执行时间:
 普通线程执行时间:
普通线程执行时间:
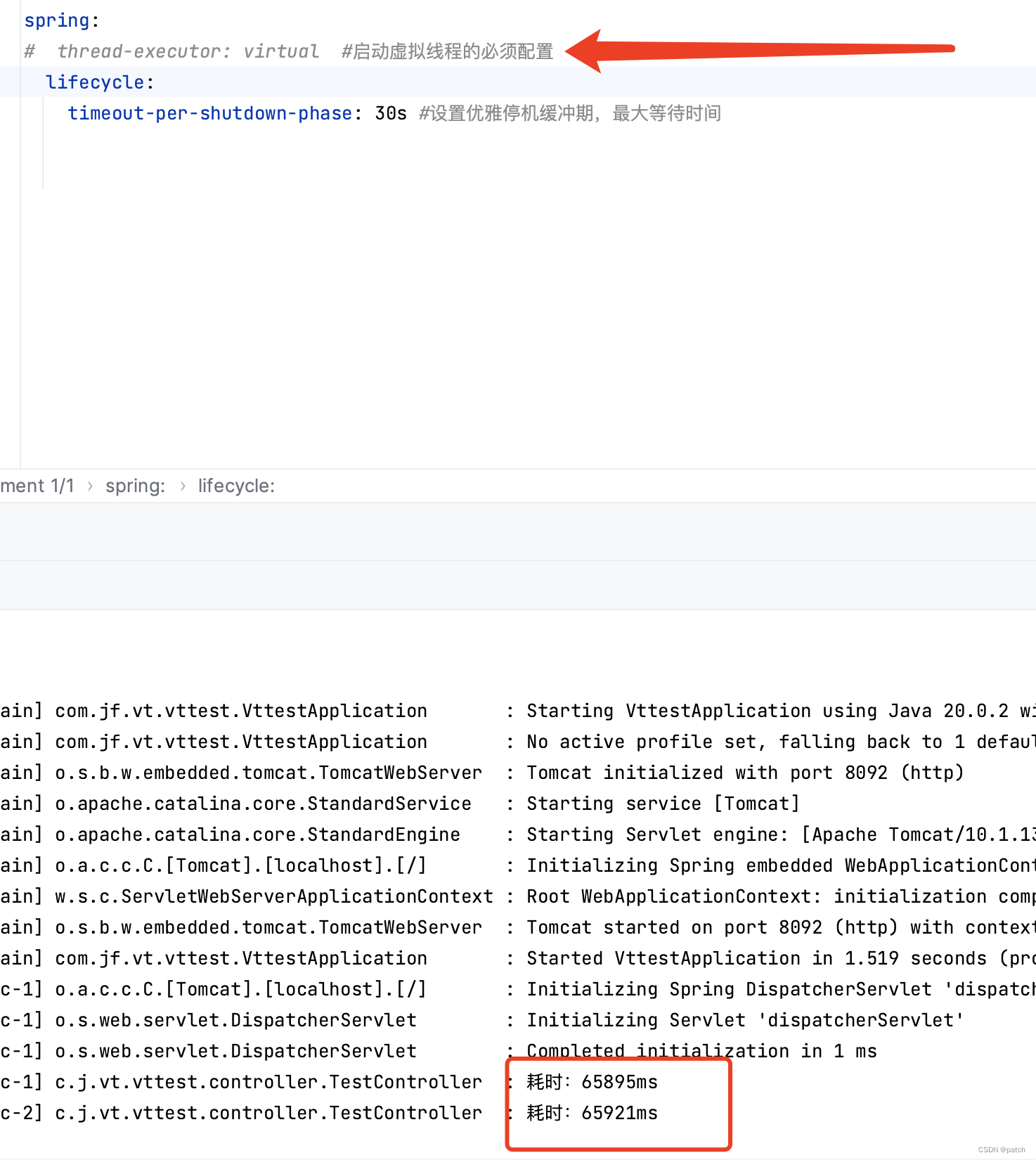 这段代码执行时间相差1000倍
这段代码执行时间相差1000倍
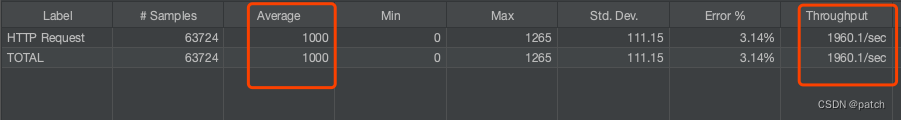
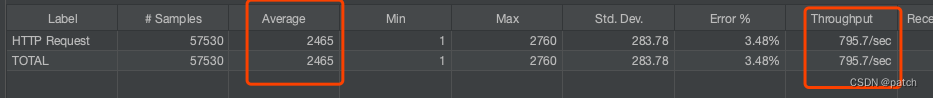
使用Jmeter压测 http://127.0.0.1:8092/test/ds 接口,吞吐量、响应时间均有大幅优化,并发数越高优化幅度越大。并发2000情况下的结果如下
虚拟线程
普通线程
参考文章:
在 Spring 6 中使用虚拟线程(Virtual Threads) - spring 中文网文章来源:https://uudwc.com/A/Xk8a5
文章来源地址https://uudwc.com/A/Xk8a5