0. 简介
我们在第三章和第四章中详细介绍了如何使用URDF以及Navigation 2,而第五章开始我们将学习如何将前面所学的结合起来,来形成一个Unity与ROS完整且系统的框架
1. 创建并导入URDF
这一部分作为我们第三讲的内容,我们在之前的基础上通过使用ROS2命令操作URDF模型增加激光传感器。具体的代码如下:toio_style.urdf
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot name="toio_style">
<!--footprint-->
<link name="base_footprint" />
<joint name="base_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="0 0 0.126" />
<parent link="base_footprint" />
<child link="base_link" />
</joint>
<!--基础坐标系-->
<link name="base_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<box size="0.3 0.3 0.23" />
</geometry>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0" />
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<box size="0.3 0.3 0.23" />
</geometry>
</collision>
<inertial>
<mass value="1.0" />
<inertia ixx="0.015" iyy="0.0375" izz="0.0375" ixy="0" ixz="0" iyz="0" />
</inertial>
</link>
<!--右车轮-->
<link name="right_wheel">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="0.05" radius="0.035" />
</geometry>
<material name="gray">
<color rgba="0.2 0.2 0.2 1" />
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="0.05" radius="0.035" />
</geometry>
</collision>
<inertial>
<mass value="0.1" />
<inertia ixx="5.1458e-5" iyy="5.1458e-5" izz="6.125e-5" ixy="0" ixz="0" iyz="0" />
</inertial>
</link>
<joint name="right_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<axis xyz="0 0 1" />
<parent link="base_link" />
<child link="right_wheel" />
<origin rpy="-1.5708 0 0" xyz="0.0 -0.125 -.09" />
</joint>
<!--左车轮-->
<link name="left_wheel">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="0.05" radius="0.035" />
</geometry>
<material name="gray" />
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="0.05" radius="0.035" />
</geometry>
</collision>
<inertial>
<mass value="0.1" />
<inertia ixx="5.1458e-5" iyy="5.1458e-5" izz="6.125e-5" ixy="0" ixz="0" iyz="0" />
</inertial>
</link>
<joint name="left_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<axis xyz="0 0 1" />
<parent link="base_link" />
<child link="left_wheel" />
<origin rpy="-1.5708 0 0" xyz="0.0 0.125 -.09" />
</joint>
<!--激光雷达-->
<link name="base_scan">
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<box size="0.1 0.1 0.1" />
</geometry>
</visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<box size="0.1 0.1 0.1" />
</geometry>
</collision>
<inertial>
<mass value="1e-5" />
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<inertia ixx="1e-6" ixy="0" ixz="0" iyy="1e-6" iyz="0" izz="1e-6" />
</inertial>
</link>
<joint name="scan_joint" type="fixed">
<axis xyz="0 1 0" />
<origin xyz="0 0 0.2" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="base_link" />
<child link="base_scan" />
</joint>
</robot>
这就构成了我们最基础的二轮激光雷达小车的结构,通过运行,来将urdf模型在rviz2中打开
ros2 launch urdf_tutorial display.launch.py model:=toio_style.urdf
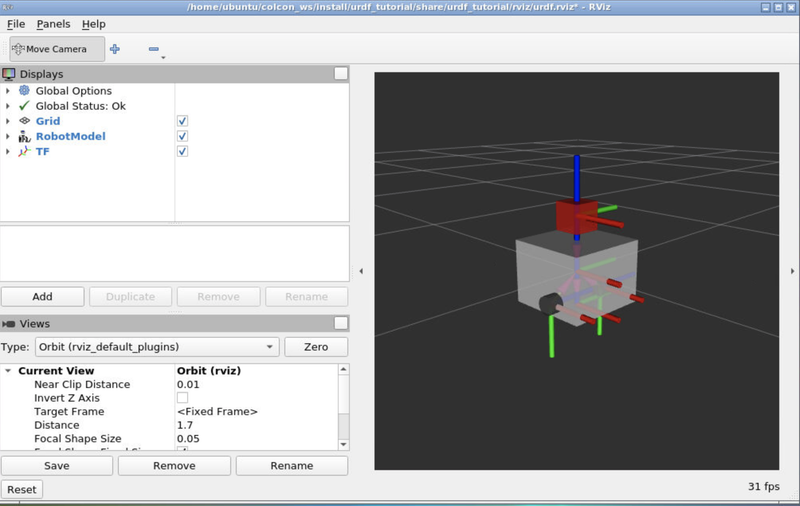
然后按照第三章讲到的导入到的几个步骤
- 启动Docker,并开放5005和10000端口
docker run -v ~/ros2_ws:/home/ubuntu/colcon_ws:cached -p 6080:80 -p 10000:10000 -p 5005:5005 --shm-size=1024m tiryoh/ros2-desktop-vnc:galactic
- 然后下载ROS-TCP-Endpoint并切换到main-ros2分支
cd ~/colcon_ws/src
git clone -b main-ros2 https://github.com/Unity-Technologies/ROS-TCP-Endpoint
- 将unity_slam_example下载到
~/colcon_ws/src。并安装nav2相关的安装包以及turtlebot3的安装包
sudo apt install ros-foxy-navigation2
sudo apt install ros-foxy-nav2-bringup
sudo apt install ros-foxy-turtlebot3*
source ~/.bashrc
- 然后将Nav2的环境变量添加到
~/.bashrc中
export TURTLEBOT3_MODEL=waffle
export GAZEBO_MODEL_PATH=$GAZEBO_MODEL_PATH:/opt/ros/foxy/share/turtlebot3_gazebo/models
source ~/.bashrc
- 然后完成编译的操作
cd ~/colcon_ws
colcon build
source ~/colcon_ws/install/setup.bash
- 在Unity的菜单“Window→Package Manager”中打开“Package Manager”。并使用→Add Package from Git URL安装以下软件包。
https://github.com/Unity-Technologies/ROS-TCP-Connector.git?path=/com.unity.robotics.ros-tcp-connector
https://github.com/Unity-Technologies/URDF-Importer.git?path=/com.unity.robotics.urdf-importer
https://github.com/Unity-Technologies/ROS-TCP-Connector.git?path=/com.unity.robotics.visualizations
- 在Unity的菜单“Robotics→ROS Settings”中指定ROS2。并将Robotics-Nav2-SLAM-Example项目中的以下Unity订阅脚本复制到项目的Assets中。并将Unity的Project窗口的“Packages/Robotics Visualization”中的DefaultVisualizationSuite拖拽到Hierarchy窗口。
・AGVController.cs
・TimeStamp.cs
・Clock.cs
・ROSClockPublisher.cs
・TransformExtensions.cs
・TransformTreeNode.cs
・ROSTransformTreePublisher.cs
・LaserScanSensor.cs
在配置完上述的内容后就可以导入URDF文件了,在Unity的Assets中导入toio_style.urdf。并选择“Import Robot Select form URDF file”。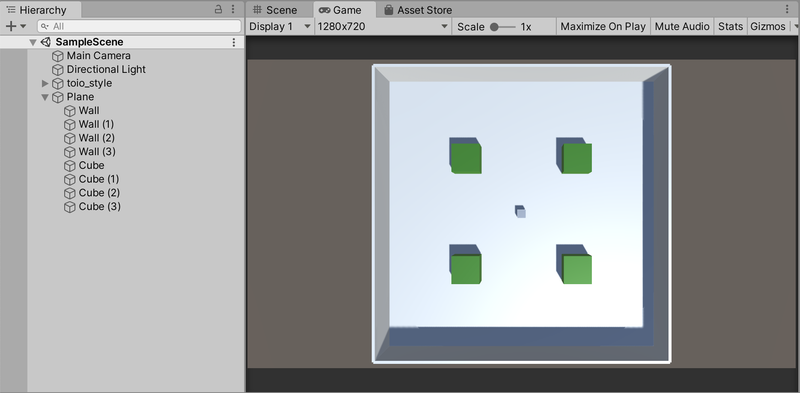
2. 添加订阅发布脚本
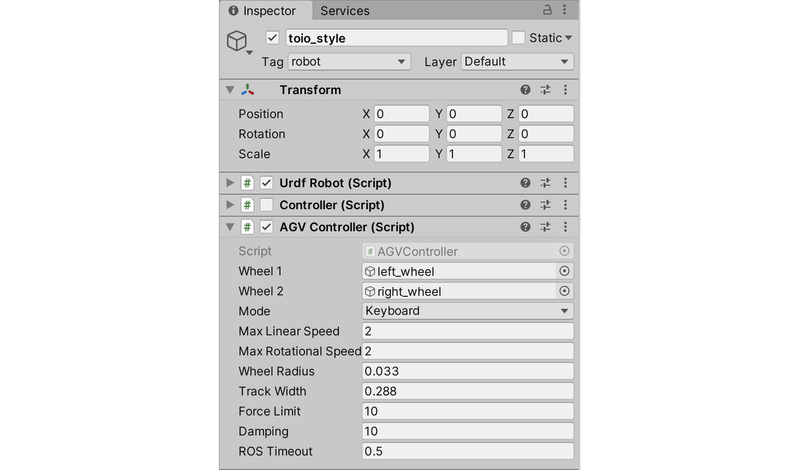
2.1 AGVController脚本添加
- 在Hierarchy窗口中选择toio_style
- 解除Controller的检查
- 在Inspector窗口中添加AGVController,设置如下
2.2 ROSPublisher订阅器添加
- 在Hierarchy窗口中,在toio_style下添加空的GameObject,并命名为“ROSPublishers”。
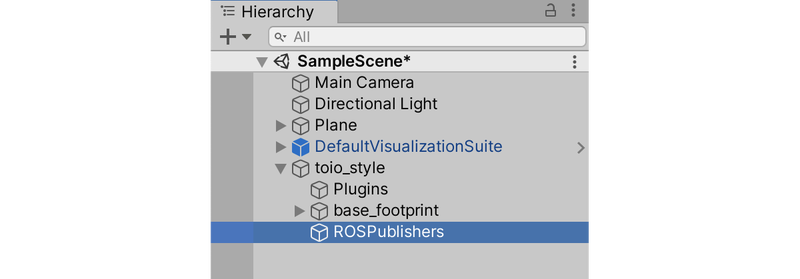
- 在Hierarchy窗口中,选择ROSPublishers这个GameObject,然后在Inspector窗口中添加ROSClockPublisher和ROSTransformTreePublisher这两个节点脚本
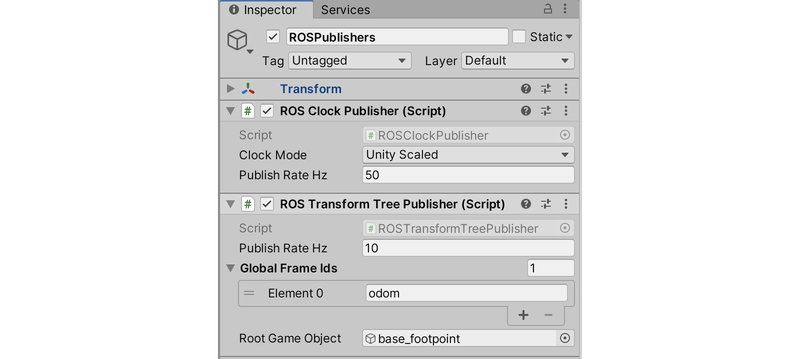
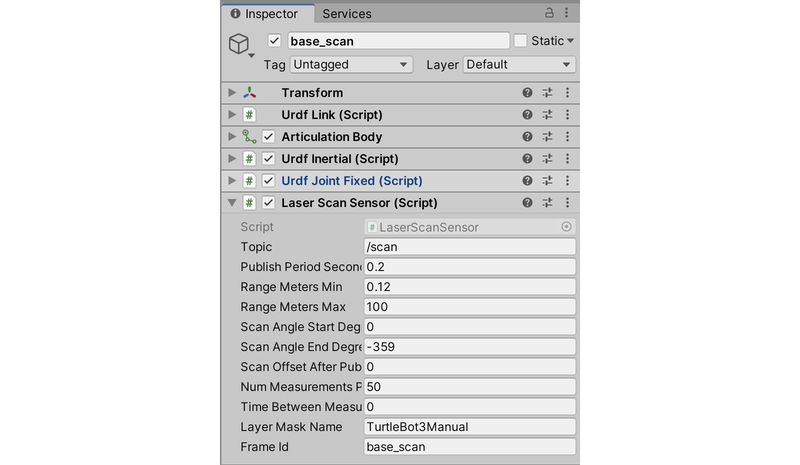
2.3 LaserScanSensor添加
-
在Hierarchy窗口中选择“toio_style→base_footprint→base_link→scan_base”
-
在Inspector窗口中添加LaserScanSensor脚本,设置如下
3. 实际运行
在ROS侧,运行启动Nav2、SLAM Toolbox和rviz2的launch文件
ros2 launch unity_slam_example unity_slam_example.py
具体代码如下文章来源:https://uudwc.com/A/aeE9
import os
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import IncludeLaunchDescription
from launch.launch_description_sources import PythonLaunchDescriptionSource
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
from launch_ros.actions import Node
def generate_launch_description():
package_name = 'unity_slam_example'
package_dir = get_package_share_directory(package_name)
return LaunchDescription({
IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource(
os.path.join(get_package_share_directory('ros_tcp_endpoint'), 'launch', 'endpoint.py')
),
),
Node(
package='rviz2',
executable='rviz2',
output='screen',
arguments=['-d', os.path.join(package_dir, 'nav2_unity.rviz')],
parameters=[{'use_sim_time':True}]
),
IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource(
os.path.join(get_package_share_directory('nav2_bringup'), 'launch', 'navigation_launch.py')
),
launch_arguments={
'use_sim_time': 'true'
}.items()
),
IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource(
os.path.join(get_package_share_directory('slam_toolbox'), 'launch', 'online_async_launch.py')
),
launch_arguments={
'use_sim_time': 'true'
}.items()
)
})
然后在Unity端,用“toio_style→AGVController”在“Mode”中指定“Keyboard”,用Play按钮执行文章来源地址https://uudwc.com/A/aeE9

