文章来源地址https://uudwc.com/A/rZzDM
环境设置:
- SentenceTransformer
- transformers
SentenceTransformers Documentation — Sentence-Transformers documentation (sbert.net)
Sentence Transformer是一个Python框架,用于句子、文本和图像嵌入Embedding。
这个框架计算超过100种语言的句子或文本嵌入。然后,这些嵌入可以进行比较,例如与余弦相似度进行比较,以找到具有相似含义的句子,这对于语义文本相似、语义搜索或释义挖掘非常有用。
该框架基于PyTorch和Transformer,并提供了大量预训练的模型集合,用于各种任务,此外,很容易微调自己的模型。
如果没有的话,利用pip安装
pip install -U sentence-transformers
pip install -U transformers
如果是conda的虚拟环境时,使用 conda 安装
可以使用以下命令安装句子转换器:conda
conda install -c conda-forge sentence-transformers关键知识点:余弦相似度计算
余弦相似度是判断两个向量相似度常用的算法,是一个向量空间中两个向量夹角间的余弦值作为衡量两个个体之间差异的大小,余弦值接近1,夹角趋于0,表明两个向量越相似,余弦值接近于0,夹角趋于90度,表明两个向量越不相似。
总之,相似度越小,距离越大。相似度越大,距离越小。
数学计算公式:
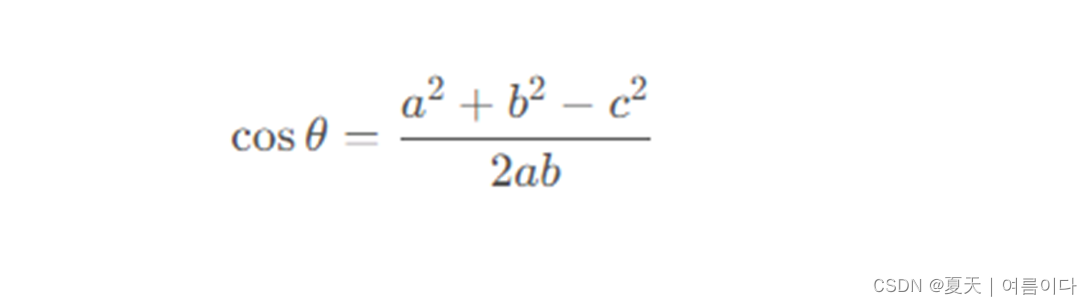
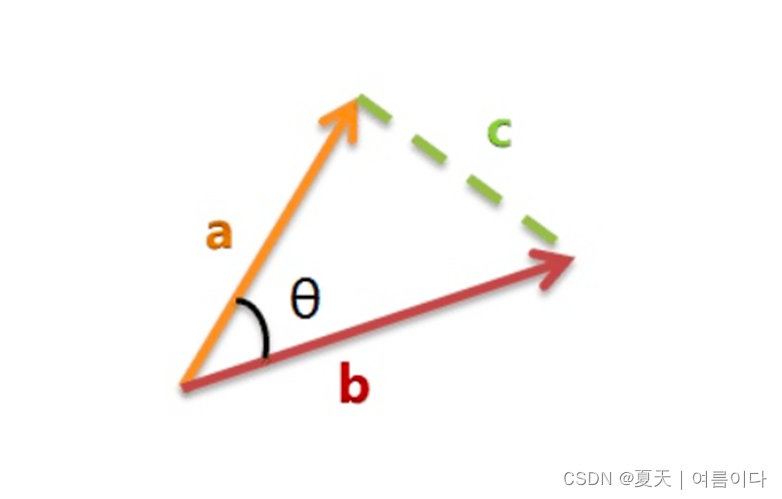
a,b,c 是三个边的长度
在NLP计算中,常用来计算词语的相似度,因为词,或者文本表示成分布式向量之后,可以很方便的计算他们的余弦相似度来评估他们的语义相似性。可以表示为
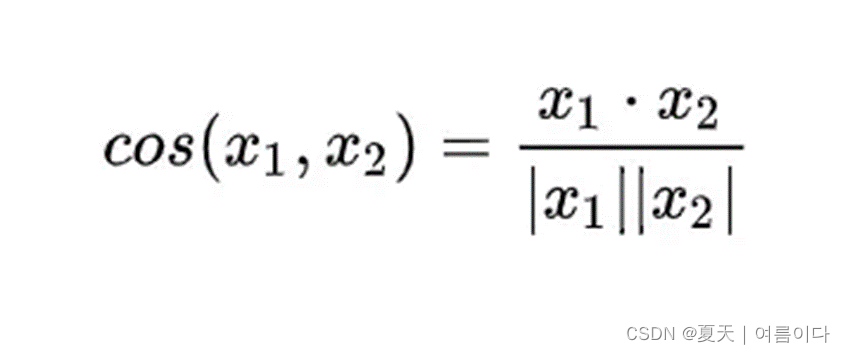
简单代码实现
# 在scipy库中计算
from scipy.spatial.distance import cosine
import numpy as np
a=np.array([1,2,3])
b=np.array([2,2,3])
print(1-cosine(a,b))#cosin() 中参数可以直接是 list
# 在sklearn库中计算矩阵
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity
a=np.array([1,2,3]).reshape(1,3)#[[1 2 3]]
b=np.array([2,2,3]).reshape(1,3)#[[2 2 3]]
c=cosine_similarity(a,b)
print('相似度结果为 : ',c)
a=np.arange(15).reshape(3,5)
b=np.arange(20).reshape(4,5)
print(a)
print(b)
c=cosine_similarity(a,b) #第一行的值是a中的每第一个行向量与b中每一个行向量之间的余弦相似度
d=cosine_similarity(a)# a 中的行向量之间的两两余弦相似度
print('c : ',c,'d : ',d)
结果如下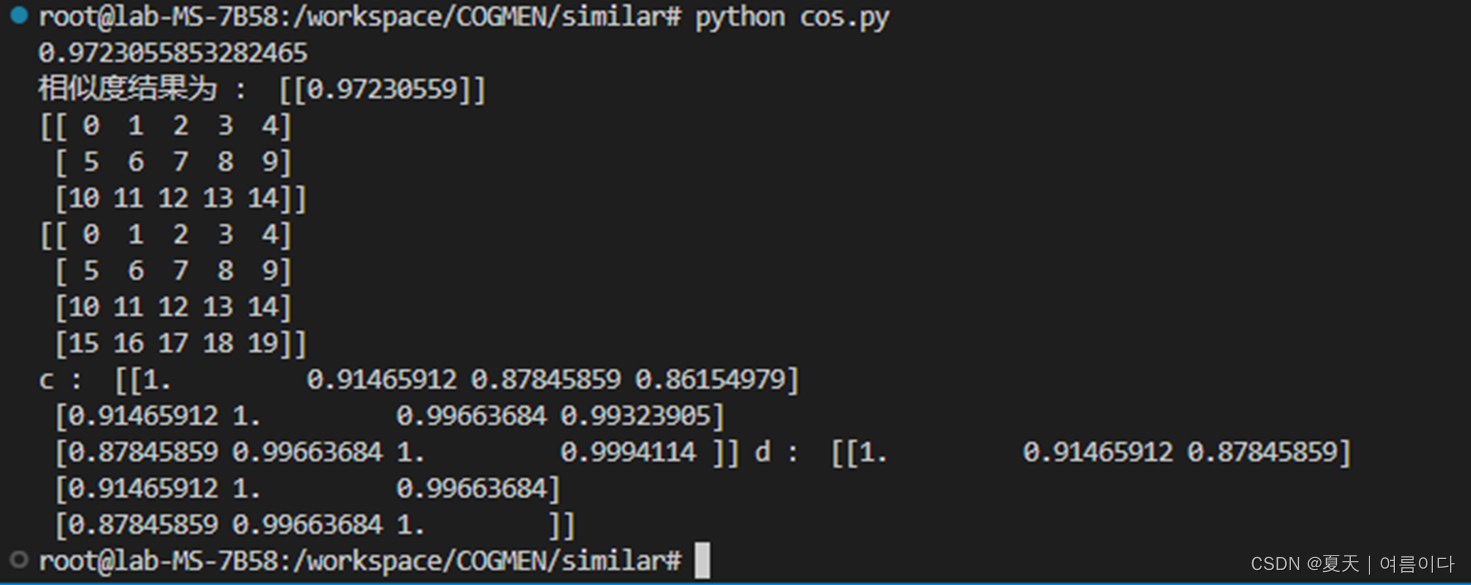
句子向量化表示
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
# Download model
model = SentenceTransformer('paraphrase-MiniLM-L6-v2')
# The sentences we'd like to encode
sentences = ['Python is an interpreted high-level general-purpose programming language.',
'Python is dynamically-typed and garbage-collected.',
'The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.']
# Get embeddings of sentences
embeddings = model.encode(sentences)
# Print the embeddings
for sentence, embedding in zip(sentences, embeddings):
print("Sentence:", sentence)
print("Embedding:", embedding)
print("")对句子进行编码,结果如下

提供各种预训练模型。使用这些模型很容易:
其中模型可更改为
model = SentenceTransformer('all-MiniLM-L6-v2')所有模型都托管在HuggingFace模型中心。
也可更改为以下预训练模型
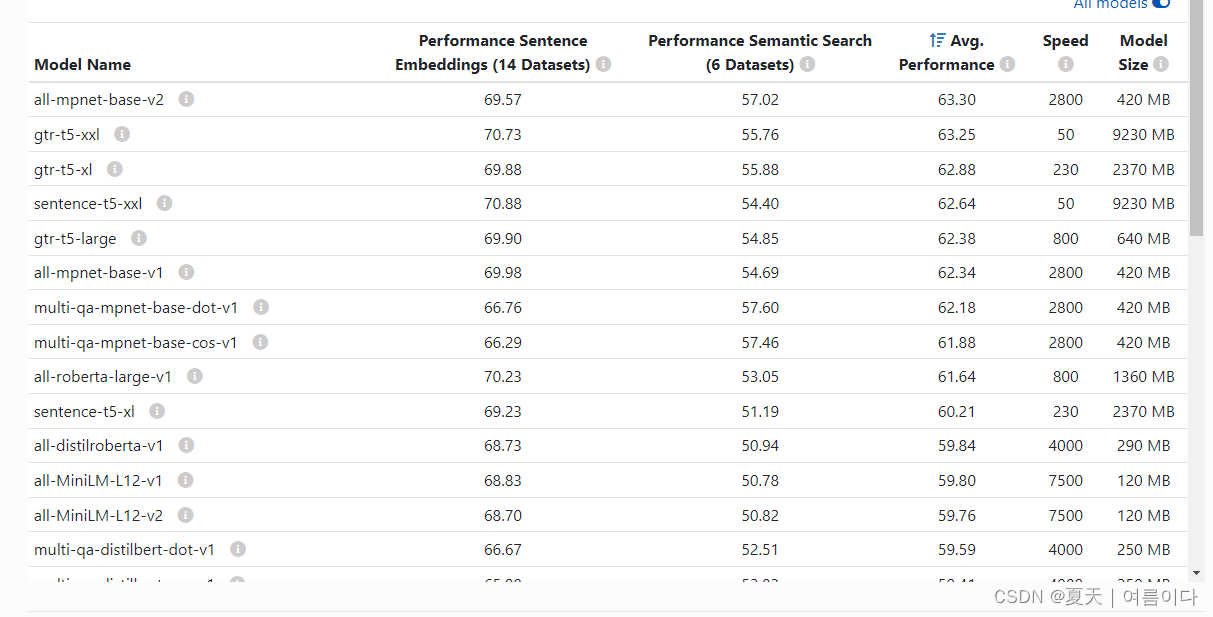
计算语义相似度
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, util
model = SentenceTransformer('all-MiniLM-L6-v2')
# 文本列表
sentences = ['The cat sits outside',
'A man is playing guitar',
'I love pasta',
'The new movie is awesome',
'The cat plays in the garden']
# 计算embeddings
embeddings = model.encode(sentences, convert_to_tensor=True)
# 计算不同文本之间的相似度
cosine_scores = util.cos_sim(embeddings, embeddings)
# 保存结果
pairs = []
for i in range(len(cosine_scores)-1):
for j in range(i+1, len(cosine_scores)):
pairs.append({'index': [i, j], 'score': cosine_scores[i][j]})
# 按照相似度分数进行排序打印
pairs = sorted(pairs, key=lambda x: x['score'], reverse=True)
for pair in pairs:
i, j = pair['index']
print("{:<30} \t\t {:<30} \t\t Score: {:.4f}".format(sentences[i], sentences[j], pair['score']))
结果如下
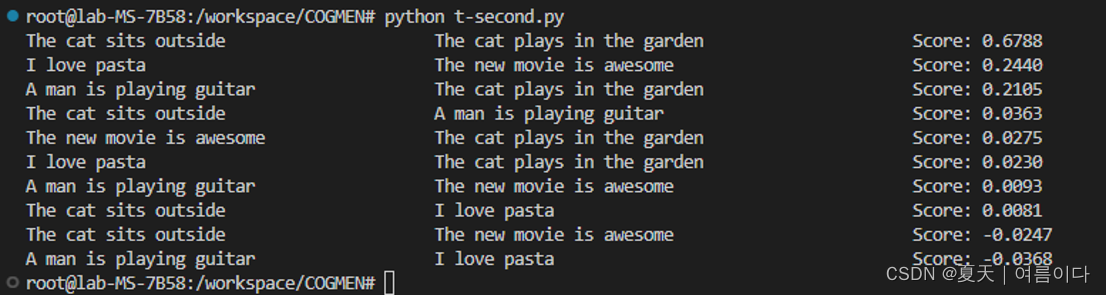
cos相似度计算
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, util
model = SentenceTransformer('all-MiniLM-L6-v2')
#Sentences are encoded by calling model.encode()
emb1 = model.encode("This is a red cat with a hat.")
emb2 = model.encode("Have you seen my red cat?")
cos_sim = util.cos_sim(emb1, emb2)
print("Cosine-Similarity:", cos_sim)结果
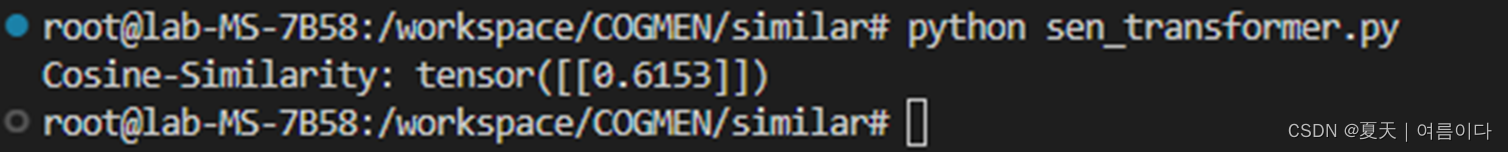
详情请参考:
Pretrained Models — Sentence-Transformers documentation (sbert.net)文章来源:https://uudwc.com/A/rZzDM