前言:
本篇文章以 TopK 问题为引,具体阐述了 PriorityQueue 实现的基本逻辑——堆 数据结构,以及PriorityQueue 的常用方法。如有问题欢迎看官朋友指正,如果觉得文章还不错的话,求点赞、收藏、评论 三连。
重点:
- 堆的基本实现逻辑
- PriorityQueue 运用和源码分析
- TopK 问题的解法
1 初识TopK问题
1.1 是什么
常见的题型是,在大小为 n 的 array 数组 中,
-
找出 前 k 个 最大 / 最小的元素
-
找出 第 k 个 最大 / 最小的元素
1.2 如何解决
无论是找到前k个,还是找到第k个,TopK 问题本质上都是找到 前k个 有序的数据集合
(文章做过些许的修改, 如有误导了各位看官朋友, 楼主深表歉意)
1)sort
- 如果是 基本数据类型,直接 Arrays.sort(array) 排序数组
- 如果是 引用数据类型,元素指向特定的对象时,在 Arrays.sort() 中再传入 Comparator 比较器再排序数组
- 然后拿到前k个有序的数据集合即可
2)快排
调用 Arrays 中自带的sort方法虽然方便,但是笔试中一般不推荐使用
- 我们可以自主实现 快速排序的方式堆数组进行排序,快排的时间复杂度最好为 O(N * logN),最坏为 O(N^2),同时快速排序后续还可以有更多的优化空间 (三数取中、区间优化、同类聚集等等),由于篇幅原因我们就不展开了
3)优先级队列
优先级队列是一种能够快速找到集合最值的数据结构, 对数据较少时进行出队入队时间复杂度很低,非常适合 TopK 问题 的解决, 相较于快速排序的 O(N * logN), O(N*logK) 数据越多优势
越明显
- 对于 TopK 问题我们可以充分利用优先级队列(堆)的特性将时间复杂度做到 O(N*logK),使排序的效果大大提升,但在这之前我们先来回顾一下有关于堆的知识吧(观众老爷们稍安勿躁),基础扎实的铁子可以直接跳转 4 解决TopK问题
2 堆
2.1 是什么
优先级队列底层是使用堆数据结构实现
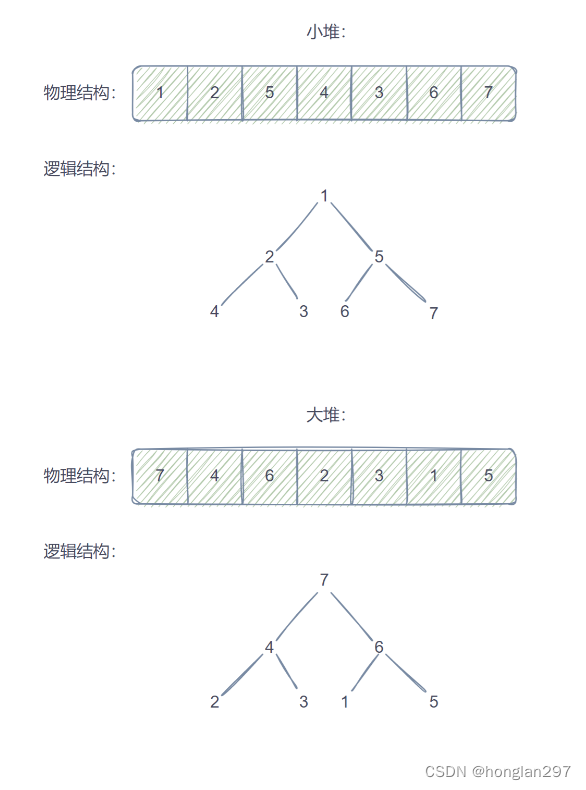
- 堆物理上 是保存在 数组 中, 逻辑上是一棵采用顺序存储方式的 完全二叉树(避免空间的浪费),通过从 0 开始的下标标定二叉树的每个节点
- 结点的值都大于其子树中结点的值,叫做大堆 / 大根堆 / 最大堆
- 结点小于子树节点叫 小堆 / 小根堆 / 最小堆,左右子节点的大小关系不能确定
- 通过首元素能够快速找到集合中的最值
2.2 堆和二叉树的顺序存储
如果有一个关键码的集合K = {k0,k1, k2,…,kn-1},把它的所有元素按完全二叉树的顺序存储方式存储 在一 个一维数组中,并满足:Ki <= K2i+1 且 Ki<= K2i+2 (Ki >= K2i+1 且 Ki >= K2i+2) i = 0,1,2…,则称为 小堆(或大堆)。
1) 存储方式
-
堆在逻辑上就是一颗完全二叉树
-
以 层序遍历 方式 用 数组保存 二叉树结构,这种方法主要用于堆的表示顺序存储存储完全二叉树,非完全二叉树会有空间的浪费
2)下标关系
起始下标为 0
(1) 已知父亲节点下标i
- 左孩节点下标:2*i + 1
- 右孩节点下标:2*i + 2
(2) 已知孩子节点下标i
- 父亲节点下标 = (child - 1)/ 2

2.3 堆的相关操作
在介绍Java 集合框架提供的 PriorityQueue 类之前,我们必须先来了解一下优先级队列常用方法背后的基本逻辑是如何的,由于优先级队列底层是使用堆数据结构实现,所以下面我们通过简单模拟实现 建堆、插入、删除、返回首元素 的操作进行详细介绍
1)建堆——向下调整
(建大根堆为例)
(1)思路:
-
传入数组,拷贝元素
-
从 最后一个节点的父节点 开始一步步向前遍历,遍历到的每一个父节点 当作一颗新树的根节点,调整该树
-
(创建新的)调整一棵树,从根节点开始,不断进行向下调整
- 找到 根节点的左右孩子中较大节点
- 根节点循环同 较大的子节点比较,进行**交换**
- 直到循环条件中根节点满足**child < len** 或者 在循环内部不满足 根节点 小于 子节点,该树调整完成
(2)解法:
public void adjustDown(int root, int len){
int parent = root;
int child = root * 2 + 1;
while(child < len){
//找到较大的孩子节点
if(child + 1 < elem.length && this.elem[child] < this.elem[child+1] ){
child++;
}
//从根节点开始向下遍历比较
if(this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]){
int tmp = elem[child];
elem[child] = elem[parent];
elem[parent] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
public void creatHeap(int[] array){
this.elem = new int[array.length];
for(int i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
this.elem[i] = array[i];
usedSize++;
}
//从最后一个节点的父节点开始调整
for(int i = (elem.length - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--){
adjustDown(i, this.elem.length);
}
}
(3)时间复杂度
以满二叉树为例:
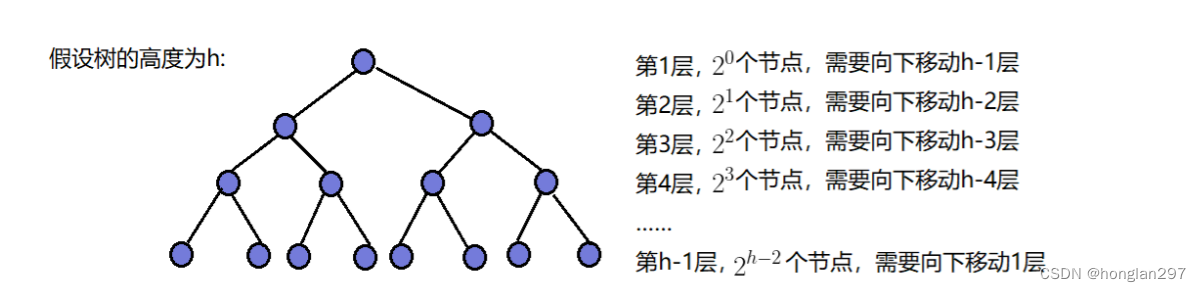

- 即时间复杂度为 O(N)
2) 插入元素——向上调整
(1)思路:
- 判满增容
- 调整,找到父节点,比较 交换或break,循环向上
(2)解决方法:
public void push(int val){
//判满
if(isFull()){
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem, 2*this.elem.length);
}
this.elem[usedSize] = val;
usedSize++;
adjustUp(this.usedSize - 1);
}
public boolean isFull(){
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}
public void adjustUp(int root){
int parent = (root - 1) / 2;
int child = root;
//从根节点的父节点循环向上调整
while(parent >= 0){
if(elem[child] > elem[parent]){
int tmp = elem[child];
elem[child] = elem[parent];
elem[parent] = tmp;
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
(3)时间复杂度:
-
最坏情况下,向上调整至首元素,调整次数为二叉树的高度 - 1
-
O(logN)
3) 删除元素——向下调整
(1)思路:
-
判空
-
将0下标元素和最后一个元素交换,删除最后一个元素,usedSize–
-
adjustDown(0,this.usedSize )向下调整
(2)解决方法:
public void poll(){
//判空
if(this.usedSize == 0){
throw new MyHeapIsEmpty("堆为空");
}
int len = this.elem.length;
int tmp = elem[0];
elem[0] = elem[len - 1];
elem[len - 1] = tmp;
this.usedSize--;
//向下调整
adjustDown(0,len - 1);
}
public void adjustDown(int root, int len){
int parent = root;
int child = root * 2 + 1;
while(child < len){
//找到较大的孩子节点
if(child + 1 < elem.length && this.elem[child] < this.elem[child+1] ){
child++;
}
//从根节点开始向下遍历比较
if(this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]){
int tmp = elem[child];
elem[child] = elem[parent];
elem[parent] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
(3)时间复杂度:
-
最坏情况下,替换的元素向下调整至二叉树最底层
-
O(logN),调整次数为二叉树的高度 - 1
4) 返回队首元素
1)思路
- 先 判空 再返回
2)解法:
public int peek(){
if(this.usedSize == 0){
throw new MyHeapIsEmpty("堆为空");
}
return this.elem[this.usedSize - 1];
}
2.4 堆排序
1)思路:
-
创建大堆
-
不断进行首尾元素交换,每次交换后向下调整同时 end–
2)解法:
public static void heapSort(int[] array){
//先创建大堆
creatHeap(array);
int end = array.length - 1;
//不断首尾交换,向下调整
while(end > 0){
int tmp = array[0];
array[0] = array[end];
array[end] = tmp;
siftDown(array, 0, end);
end--;
}
}
public static void creatHeap(int[] array){
for(int i = (array.length - 1 - 1) / 2 ; i >= 0; i--){
siftDown(array, i, array.length);
}
}
public static void siftDown(int[] array, int root, int len){
int parent = root;
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while(child < len) {
if (child + 1 < len && array[child] < array[child + 1]) {
child++;
}
if (array[child] > array[parent]) {
int tmp = array[child];
array[child] = array[parent];
array[parent] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
3)时间复杂度:
-
创建大堆时间复杂度为 O(N),首尾交换向下调整时间复杂度为 N * logN,
-
两者是并列关系,最终时间复杂度为 O(N*logN)
3 优先级队列
由 Java 提供的 PriorityQueue 和 PriorityBlockingQueue 两种优先级队列供我们使用,都继承于 Queue集合类
我们主要介绍PriorityQueue,下面主要介绍常用的构造方法 、成员变量,结合部分源码剖析一下优先级队列的 offer 成员方法,其他的成员方法我们只需会使用即可
3.1 构造方法PriorityQueue()
-
PriorityQueue()
-
PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity)
- 指定初始容量
-
public PriorityQueue(Comparator<? super E> comparator)
- 传入比较器
-
public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity, Comparator<? super E> comparator)
- 指定initialCapacity 不能 < 1,否则会抛出异常
- 指定initialCapacity 不能 < 1,否则会抛出异常
3.2 成员变量
-
Object[] queue
-
int size
-
Comparator<? super E> comparator
3.3 成员方法
| 方法名 | 详情 |
|---|---|
| boolean offer (E e) | 插入元素,元素为空抛出异常 |
| E peek () | 得到集合中的最值(优先级最高元素) |
| E poll () | 删除集合中的最值(优先级最高元素) |
| int size () | 得到元素个数 |
| boolean isEmpty () | 判断队列是否为空 |
| void clear () | 清除元素 |
1)offer 源码

(1)扩容判断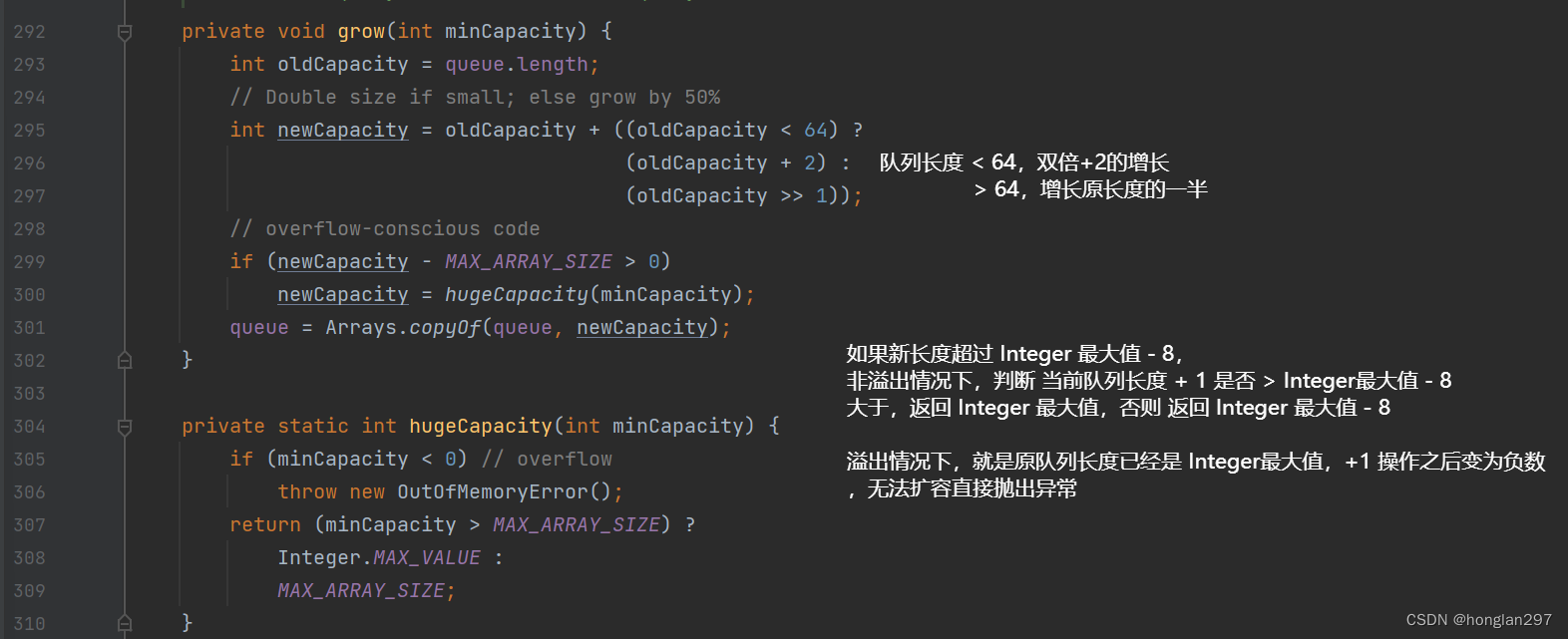
(2)第一次插入
直接赋值
(3)非第一次插入

是否有比较器
-
是

-
否
没有比较器,传入的对象也要重写 Compare 方法

-
如果传入的是 Integer类,其重写compareTo方法将插入元素x 和 父元素 e 进行比较,是 默认建立小根堆
this.value 表示插入元素


3.4 PriorityQueue 创建大根堆
PriorityQueue 默认创建的是小根堆,但是在具体的应用场景中我们必须创建大根堆来寻求题解(诸如经典 TopK 问题中找到数组中前K个小的数字)
- 已有类型,构造优先级队列时直接 传入比较器,重写compare时,return o2 - o1(o2表示父元素),即父元素值大于传入元素值直接停止向上调整
- 自定义类型,记得 实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo方法
- 建立大根堆 return o2 - o1,
- 建立小根堆 return o1 - o2
4 解决TopK问题
4.1 解决TopK问题
以找前k个最小的元素为例
1)思路:
-
找前 k 小的元素,创建大根堆maxHeap
- 在构造PriorityQueue 时 需要传入比较器,因为PriorityQueue默认是创建小根堆
如果构造的时候传入k,要先 判断k是否 <1
- 在构造PriorityQueue 时 需要传入比较器,因为PriorityQueue默认是创建小根堆
-
遍历array数组,当 i < k,放入array[i] 到maxHeap
-
遍历array数组,当 i >= k,获取 堆中最大元素 tmp,tmp 同array[i]比较
- 当 array[i] < tmp,先出队除去tmp,再入队将array[i] 放入maxHeap中
2)解法:
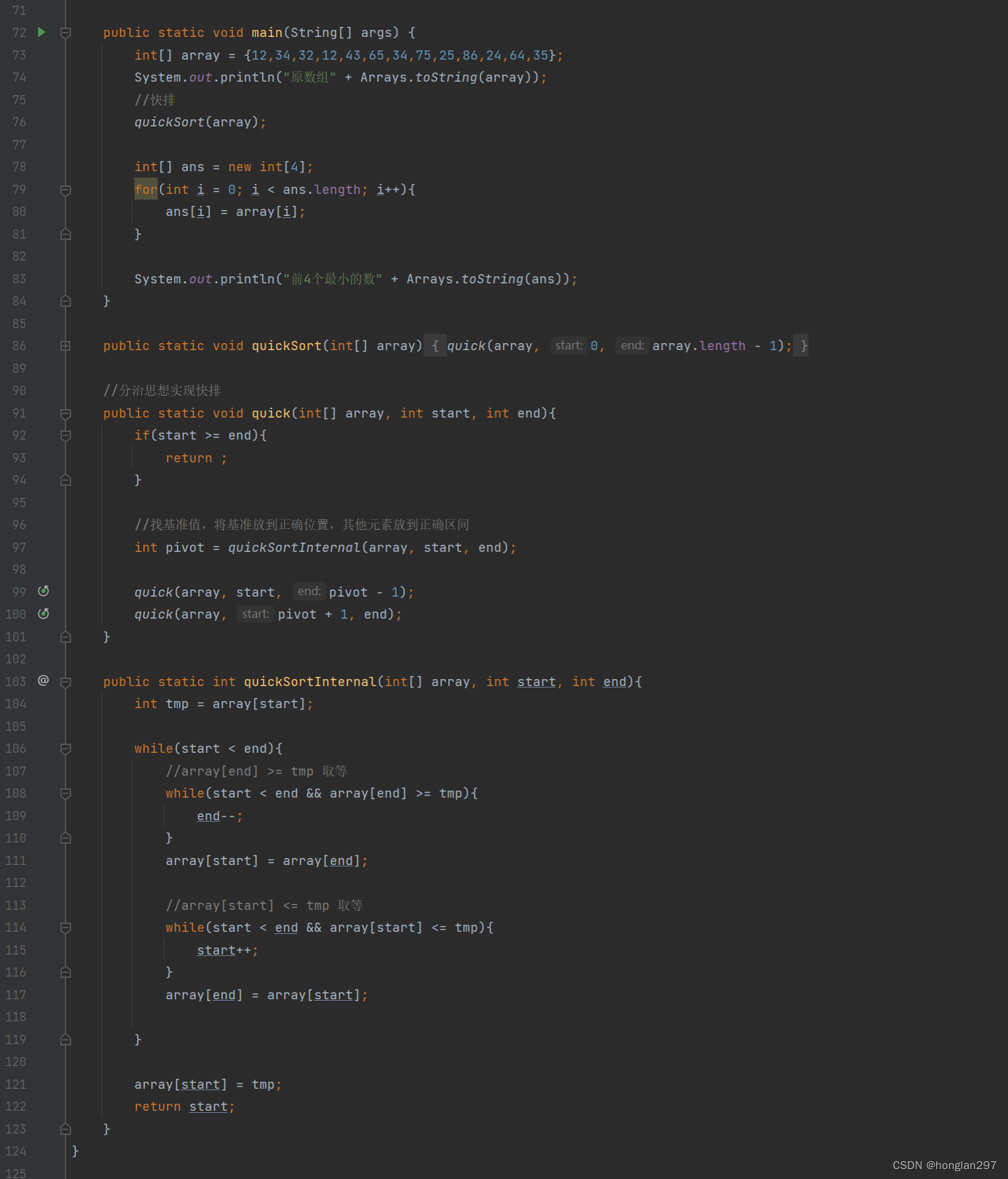
- 前k个最小的元素
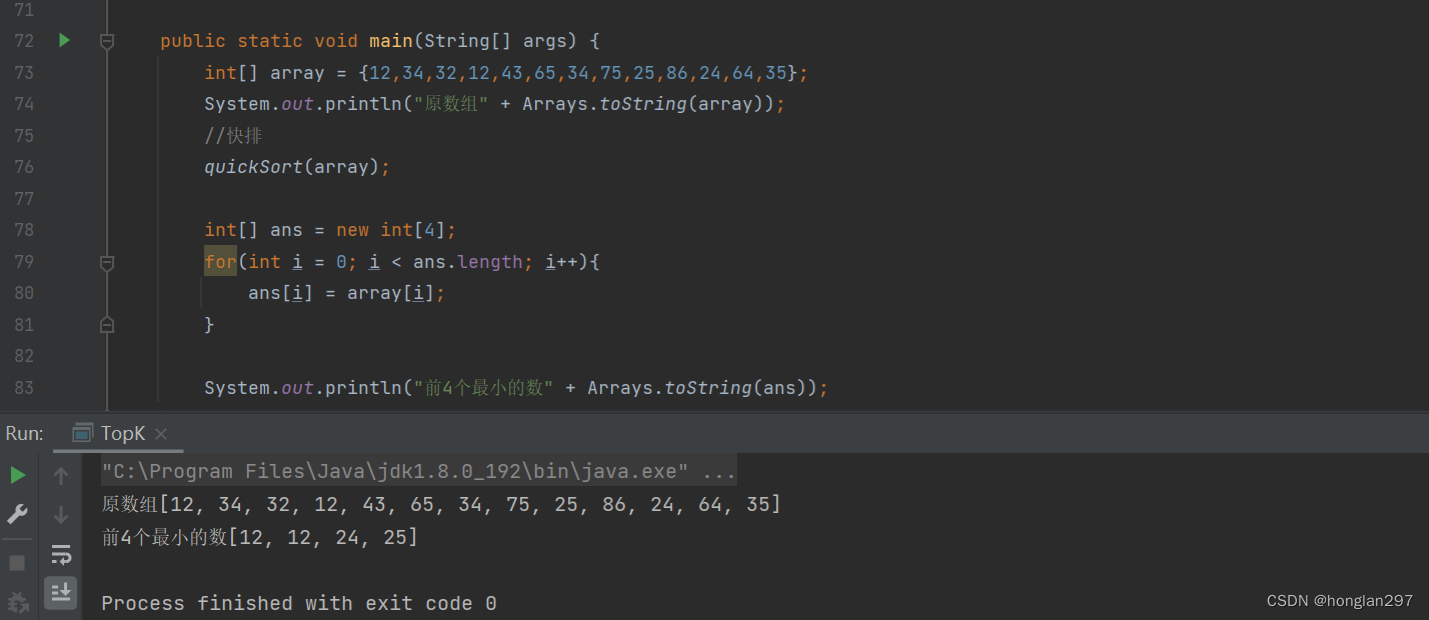
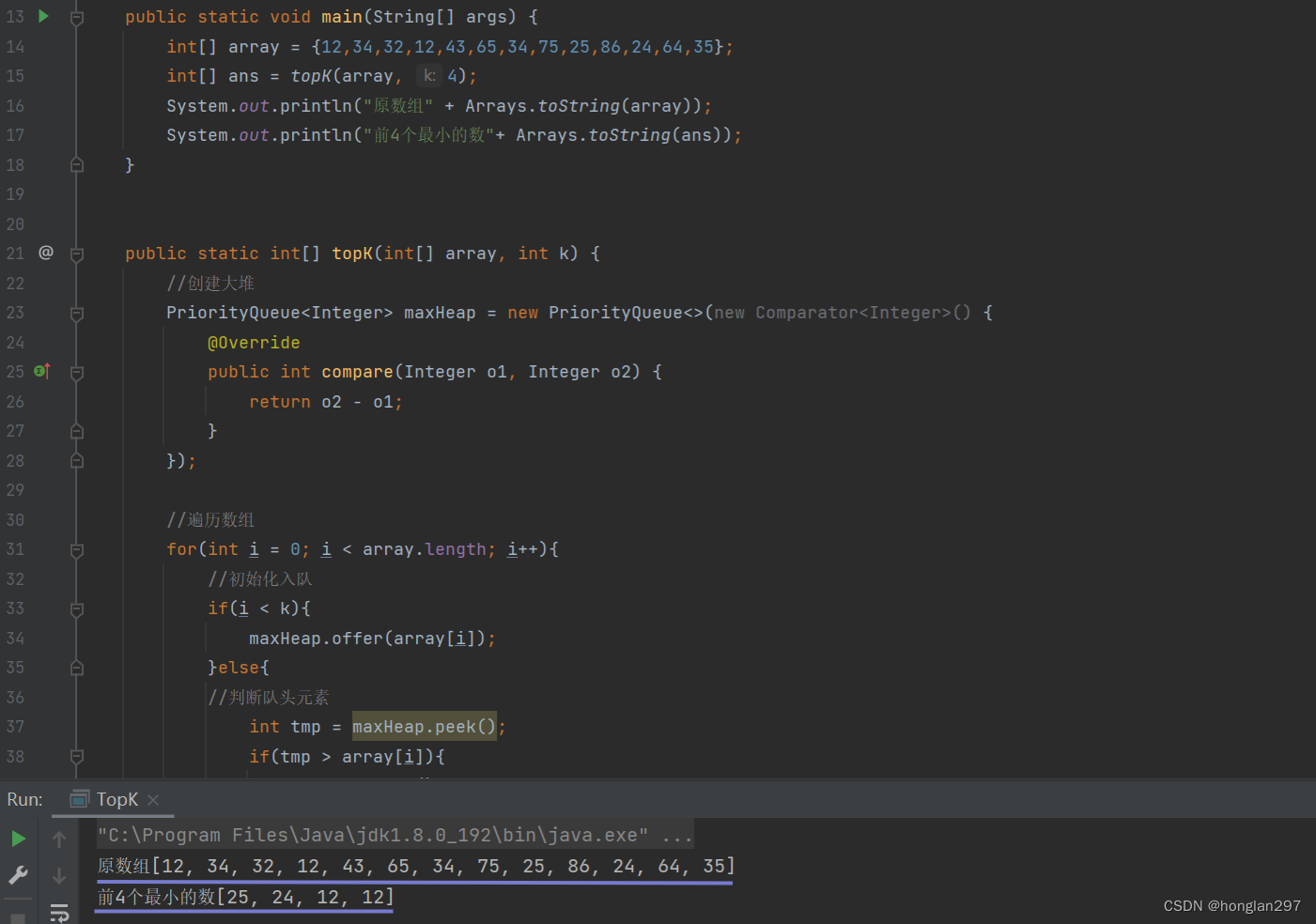
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,34,32,12,43,65,34,75,25,86,24,64,35};
int[] ans = topK(array, 4);
System.out.println("原数组" + Arrays.toString(array));
System.out.println("前4个最小的数"+ Arrays.toString(ans));
}
public static int[] topK(int[] array, int k) {
//创建大堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
});
//遍历数组
for(int i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
//初始化入队
if(i < k){
maxHeap.offer(array[i]);
}else{
//判断队头元素
int tmp = maxHeap.peek();
if(tmp > array[i]){
maxHeap.poll();
maxHeap.offer(array[i]);
}
}
}
//maxHeap顺序放入ans数组返回
int[] ans = new int[k];
int count = 0;
while(!maxHeap.isEmpty()){
ans[count++] = maxHeap.poll();
}
return ans;
}
- 结果
3)时间复杂度
- 最坏情况下,初始化入队遍历 N 个元素都需要更换队头元素操作,出队入队时间复杂度为 2*logK,
- 所以时间复杂度为 O(N * logK)
4.2 TopK相关练习
查找和最小的 K 对数字
1)思路
-
实例化元素类型为 List的堆,调用带有**k, 比较器 2个参数的构造方法**
-
两层循环拿到每一个对值,判断是否**入队** 或者 更换队头元素文章来源:https://uudwc.com/A/wRjW
- 创建临时 List list 接收对值
- 判断list 是否**放入堆** 中 或者 更换队头元素
-
遍历堆元素放入 List<List> 的 List文章来源地址https://uudwc.com/A/wRjW
2)解法
public List<List<Integer>> kSmallestPairs(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k) {
//创建大堆
PriorityQueue<List<Integer>> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(k, new omparator<List<Integer>>() {
@Override
public int compare(List<Integer> o1, List<Integer> o2) {
return (o2.get(0) + o2.get(1)) - (o1.get(0) + o1.get(1));
}
});
//遍历数组
for(int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < nums2.length; j++){
//直接放入堆
if(maxHeap.size() < k){
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(nums1[i]);
list.add(nums2[j]);
maxHeap.offer(list);
//更换队头元素
}else{
List<Integer> top = maxHeap.peek();
int topval = top.get(0) + top.get(1);
if(topval > nums1[i] + nums2[j]){
maxHeap.poll();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(nums1[i]);
list.add(nums2[j]);
maxHeap.offer(list);
}
}
}
}
//放回 List<List<Integer>>
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < k && !maxHeap.isEmpty(); i++){
ret.add(maxHeap.poll());
}
return ret;
}