文章目录
- 参考:
- 总结
- [CSP-J2020] 优秀的拆分
- 题目描述
- 输入格式
- 输出格式
- 样例 #1
- 样例输入 #1
- 样例输出 #1
- 样例 #2
- 样例输入 #2
- 样例输出 #2
- 提示
- 样例 1 解释
- 数据规模与约定
- 答案1
- 答案2
- [CSP-J2020] 直播获奖
- 题目描述
- 输入格式
- 输出格式
- 样例 #1
- 样例输入 #1
- 样例输出 #1
- 样例 #2
- 样例输入 #2
- 样例输出 #2
- 提示
- 样例 1 解释
- 数据规模与约定
- 提示
- 答案1
- 答案2
- 现场真题注意事项

参考:
P7071 [CSP-J2020] 优秀的拆分
P7072 [CSP-J2020] 直播获奖
总结
本系列为CSP-J/S算法竞赛真题讲解,会按照年份分析每年的真题,并给出对应的答案。本文为2020年真题。
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/list?tag=343&page=1
[CSP-J2020] 优秀的拆分
题目描述
一般来说,一个正整数可以拆分成若干个正整数的和。
例如, 1 = 1 1=1 1=1, 10 = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 10=1+2+3+4 10=1+2+3+4 等。对于正整数 n n n 的一种特定拆分,我们称它为“优秀的”,当且仅当在这种拆分下, n n n 被分解为了若干个不同的 2 2 2 的正整数次幂。注意,一个数 x x x 能被表示成 2 2 2 的正整数次幂,当且仅当 x x x 能通过正整数个 2 2 2 相乘在一起得到。
例如, 10 = 8 + 2 = 2 3 + 2 1 10=8+2=2^3+2^1 10=8+2=23+21 是一个优秀的拆分。但是, 7 = 4 + 2 + 1 = 2 2 + 2 1 + 2 0 7=4+2+1=2^2+2^1+2^0 7=4+2+1=22+21+20 就不是一个优秀的拆分,因为 1 1 1 不是 2 2 2 的正整数次幂。
现在,给定正整数 n n n,你需要判断这个数的所有拆分中,是否存在优秀的拆分。若存在,请你给出具体的拆分方案。
输入格式
输入只有一行,一个整数 n n n,代表需要判断的数。
输出格式
如果这个数的所有拆分中,存在优秀的拆分。那么,你需要从大到小输出这个拆分中的每一个数,相邻两个数之间用一个空格隔开。可以证明,在规定了拆分数字的顺序后,该拆分方案是唯一的。
若不存在优秀的拆分,输出 -1。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
6
样例输出 #1
4 2
样例 #2
样例输入 #2
7
样例输出 #2
-1
提示
样例 1 解释
6 = 4 + 2 = 2 2 + 2 1 6=4+2=2^2+2^1 6=4+2=22+21 是一个优秀的拆分。注意, 6 = 2 + 2 + 2 6=2+2+2 6=2+2+2 不是一个优秀的拆分,因为拆分成的 3 3 3 个数不满足每个数互不相同。
数据规模与约定
- 对于 20 % 20\% 20% 的数据, n ≤ 10 n \le 10 n≤10。
- 对于另外 20 % 20\% 20% 的数据,保证 n n n 为奇数。
- 对于另外 20 % 20\% 20% 的数据,保证 n n n 为 2 2 2 的正整数次幂。
- 对于 80 % 80\% 80% 的数据, n ≤ 1024 n \le 1024 n≤1024。
- 对于 100 % 100\% 100% 的数据, 1 ≤ n ≤ 10 7 1 \le n \le {10}^7 1≤n≤107。
答案1
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include<cstdio>//必须包含cstdio头文件
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath> //pow
using namespace std;
int n;
int a[110];//a[i]=1表示第i位上是1 pow(2,i)
int len;
int main(){
//freopen("candy.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("candy.out","w",stdout);
cin>>n;
if(n%2!=0){
cout<<-1<<endl;
return 0;
}
while(n){ //把十进制转换为二进制
a[len++]=n%2;
n/=2;
}
for(int i=len;i>=0;i--){
if(a[i]){
int x = pow(2,i);
cout<<x<<" ";
}
}
//system("pause");
//fclose(stdin);
//fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
答案2
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include<cstdio>//必须包含cstdio头文件
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath> //pow
using namespace std;
int n;
int a[32];//a[i]表示第i位上是 pow(2,i)
int main(){
//freopen("candy.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("candy.out","w",stdout);
for(int i=0;i<31;i++){
a[i]=pow(2,i);
}
cin>>n;
if(n%2!=0){
cout<<-1;
return 0;
}
for(int i=30;i>=0;i--){
if(n>=a[i]){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
n -= a[i];
}
}
//system("pause");
//fclose(stdin);
//fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
[CSP-J2020] 直播获奖
题目描述
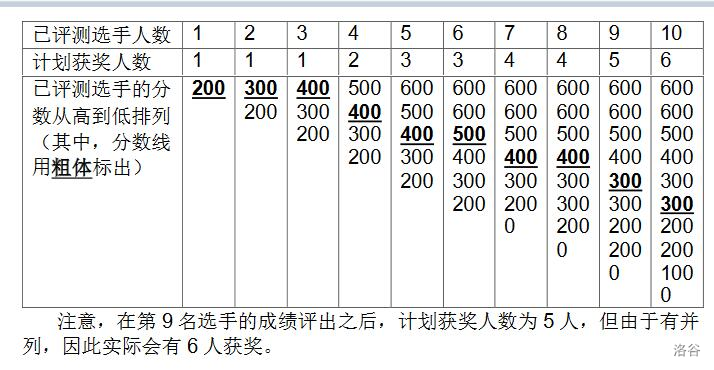
NOI2130 即将举行。为了增加观赏性,CCF 决定逐一评出每个选手的成绩,并直播即时的获奖分数线。本次竞赛的获奖率为 w % w\% w%,即当前排名前 w % w\% w% 的选手的最低成绩就是即时的分数线。
更具体地,若当前已评出了 p p p 个选手的成绩,则当前计划获奖人数为 max ( 1 , ⌊ p × w % ⌋ ) \max(1, \lfloor p \times w \%\rfloor) max(1,⌊p×w%⌋),其中 w w w 是获奖百分比, ⌊ x ⌋ \lfloor x \rfloor ⌊x⌋ 表示对 x x x 向下取整, max ( x , y ) \max(x,y) max(x,y) 表示 x x x 和 y y y 中较大的数。如有选手成绩相同,则所有成绩并列的选手都能获奖,因此实际获奖人数可能比计划中多。
作为评测组的技术人员,请你帮 CCF 写一个直播程序。
输入格式
第一行有两个整数
n
,
w
n, w
n,w。分别代表选手总数与获奖率。
第二行有
n
n
n 个整数,依次代表逐一评出的选手成绩。
输出格式
只有一行,包含 n n n 个非负整数,依次代表选手成绩逐一评出后,即时的获奖分数线。相邻两个整数间用一个空格分隔。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
10 60
200 300 400 500 600 600 0 300 200 100
样例输出 #1
200 300 400 400 400 500 400 400 300 300
样例 #2
样例输入 #2
10 30
100 100 600 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
样例输出 #2
100 100 600 600 600 600 100 100 100 100
提示
样例 1 解释
数据规模与约定
各测试点的 n n n 如下表:
| 测试点编号 | n = n= n= |
|---|---|
| 1 ∼ 3 1 \sim 3 1∼3 | 10 10 10 |
| 4 ∼ 6 4 \sim 6 4∼6 | 500 500 500 |
| 7 ∼ 10 7 \sim 10 7∼10 | 2000 2000 2000 |
| 11 ∼ 17 11 \sim 17 11∼17 | 1 0 4 10^4 104 |
| 18 ∼ 20 18 \sim 20 18∼20 | 1 0 5 10^5 105 |
对于所有测试点,每个选手的成绩均为不超过 600 600 600 的非负整数,获奖百分比 w w w 是一个正整数且 1 ≤ w ≤ 99 1 \le w \le 99 1≤w≤99。
提示
在计算计划获奖人数时,如用浮点类型的变量(如 C/C++ 中的 float 、 double,Pascal 中的 real 、 double 、 extended 等)存储获奖比例
w
%
w\%
w%,则计算
5
×
60
%
5 \times 60\%
5×60% 时的结果可能为
3.000001
3.000001
3.000001,也可能为
2.999999
2.999999
2.999999,向下取整后的结果不确定。因此,建议仅使用整型变量,以计算出准确值。
答案1
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include<cstdio>//必须包含cstdio头文件
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm> //sort排序
//#include<cmath> //pow
using namespace std;
int n,w;//n为人数 w为比例
int a[100010];
bool cmp(int x,int y){
return x>y;
}
int main(){
//freopen("candy.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("candy.out","w",stdout);
cin>>n>>w;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
sort(a+1,a+1+i,cmp);
int t = 1.0*i*w/100;
int p = max(1,t);
cout<<a[p] <<" ";
}
//system("pause");
//fclose(stdin);
//fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}

答案2
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include<cstdio>//必须包含cstdio头文件
#include<iostream>
//#include<algorithm> //sort排序
//#include<cmath> //pow
using namespace std;
int n,w;//n为人数 w为比例
int a[1010];//1010个桶 a[i]表示i分的人数
int main(){
//freopen("candy.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("candy.out","w",stdout);
cin>>n>>w;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int x;
cin>>x;
a[x]++;
int t=1.0*i*w/100;
int p=max(1,t);
int sum=0;
for(int j=600;j>=0;j--){
if(sum + a[j]>=p){
cout<<j<<" ";
break;
}
sum += a[j];
}
}
//system("pause");
//fclose(stdin);
//fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
现场真题注意事项
https://cspoj.com/contest.php?cid=1002
Fus5yz4x3EcSJH1Z
注意事项
- 文件名(程序名和输入输出文件名)必须使用英文小写。(提交必须使用freopen()进行提交)
- C/C++ 中函数 main() 的返回值类型必须是 int,程序正常结束时的返回值必须是0。
- 提交的程序代码文件的放置位置请参考各省的具体要求。
- 因违反以上三点而出现的错误或问题,申述时一律不予受理。
- 若无特殊说明,结果的比较方式为全文比较(过滤行末空格及文末回车)。
- 程序可使用的栈空间内存限制与题目的内存限制一致。
- 全国统一评测时采用的机器配置为:Inter® Core™ i7-8700K CPU @3.70GHz,内存 32GB。上述时限以此配置为准。
- 只提供 Linux 格式附加样例文件。
- 评测在当前最新公布的 NOI Linux 下进行,各语言的编译器版本以此为准
/*
假设输入样例数据存在文件test.in中,输出样例数据存在文件test.out中,
则在CSP、NOI等比赛的代码中,需添加freopen、fclose语句,
内容详见模板代码如下。
*/文章来源:https://uudwc.com/A/xG55n
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include<cstdio>//必须包含cstdio头文件
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
freopen("test.in","r",stdin);
freopen("test.out","w",stdout);
cout<<"Hello NOI"<<endl;
fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
下面为函数的简介,详细可参见 http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/clibrary/cstdio/freopen.html
函数名:freopen
声明:FILE *freopen( const char *path, const char *mode, FILE *stream );
所在文件: stdio.h
参数说明:
path: 文件名,用于存储输入输出的自定义文件名。
mode: 文件打开的模式。和fopen中的模式(如r-只读, w-写)相同。
stream: 一个文件,通常使用标准流文件。
返回值:成功,则返回一个path所指定文件的指针;失败,返回NULL。(一般可以不使用它的返回值)
功能:实现重定向,把预定义的标准流文件定向到由path指定的文件中。标准流文件具体是指stdin、stdout和stderr。其中stdin是标准输入流,默认为键盘;stdout是标准输出流,默认为屏幕;stderr是标准错误流,一般把屏幕设为默认。通过调用freopen,就可以修改标准流文件的默认值,实现重定向。文章来源地址https://uudwc.com/A/xG55n
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main(){
freopen("7532.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("7532.out", "w", stdout);
//原来的代码保持不变
double a, b, r;
int k;
cin >> a >> b;
k = int(a/b);
r = a - b * k;
printf("%g", r);
//-------------
fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
