写在前面:本章主要理解加法器和减法器的概念,并了解 Code converter 的概念。使用 Verilog 实现多种加法器、减法器和代码转换器,通过 FPGA 验证 Verilog 实现的电路的行为。
 本篇博客全站热榜排名:12
本篇博客全站热榜排名:12
Ⅰ. 前置知识
0x00 半加器与全加器
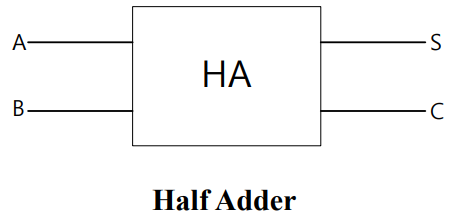
① 半加器 () 有两个输入和输出:
- 输入由 2 个 1-bit
数组成,输出由
和
组成。
- 当两个 1-bit 数相加大于可以用 1-bit 表示的数时,会生成进位(Carry)。
② 全加器()是 Carry 也是一个可加的加法器,用作实际的基础运算电路。

0x01 半减器与全减器
减法器与加法器相反,是用于 1-bit 数减法的逻辑电路。
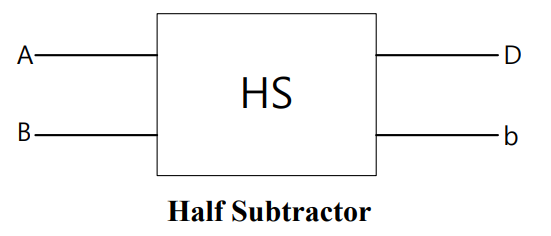
半减器 () 由
和
组成,分别表示两个 1-bit 输入
和输出
的结果。
如果要进行比一个数字更大的减法,则从前面的数字中获取借位(Borrow)。
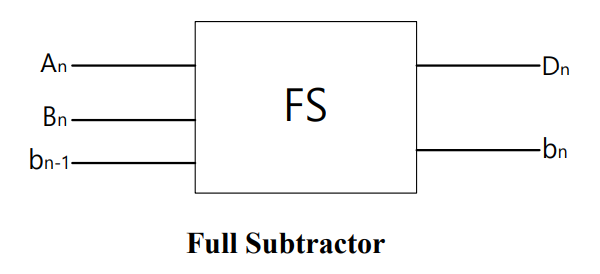
全减器 () 将 Borrow 也作为输入,具有完整的 Subtractor 功能:
0x02 逻辑电路设计程序
设计程序:
- 考虑电路的结构和动作,用真值表进行设计。
- 将真值表的内容转换为卡诺图(K-map)。
- 通过编写的卡诺图和的 Minimization (
,
) ,编写出最小化形式的布尔函数。
- 尽量使用
或
门进行配置。
- 验证配置和实验结果是否与真值表相同。
Code Converter:一种逻辑电路,它将输入的特定代码转换成指定的代码输出。
Ⅱ. 练习(Assignment)
练习1:Half Adder
按照下列结构写出 Verilog 代码,得到 Verilog 的 Simulation 结果。
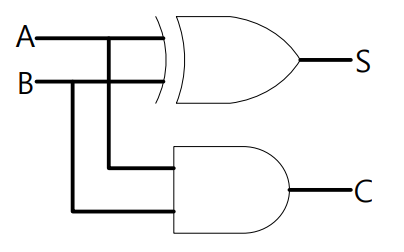
? Design source:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
/* Half_Adder */
module Half_Adder (
input a, b,
output s, c
);
assign s = a ^ b;
assign c = a & b;
endmodule? Testbench:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
/* Half_Adder Table Bench */
module Half_Adder_tb;
reg aa, bb;
wire s, c;
Half_Adder u_Half_Adder(
.a(aa),
.b(bb),
.s(s),
.c(c)
);
initial aa = 1'b0;
initial bb = 1'b0;
always aa = #100 ~aa;
always bb = #200 ~bb;
initial begin
#1000
$finish;
end
endmodule
? 运行结果如下:
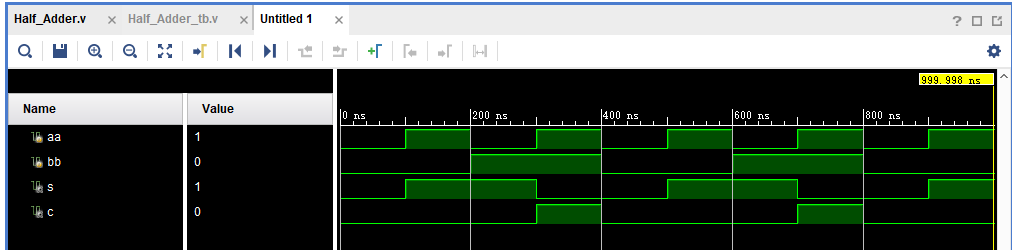
练习2:Full Adder
按照下列结构写出 Verilog 代码,得到 Verilog 的 Simulation 结果。

? Design source:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
/* Full_Adder */
module Full_Adder (
input a, b, cinput,
output s, coutput
);
assign s = (a ^ b) ^ cinput;
assign coutput = (a & b) | ((a ^ b) & cinput);
endmodule? Testbench:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
/* Full_Adder Sim */
module Full_Adder_tb;
reg aa, bb, ccinput;
wire s, coutput;
Full_Adder u_Full_Adder (
.a(aa),
.b(bb),
.cinput(ccinput),
.s(s),
.coutput(coutput)
);
initial aa = 1'b0;
initial bb = 1'b0;
initial ccinput = 1'b0;
always aa = #100 ~aa;
always bb = #200 ~bb;
always ccinput = #400 ~ccinput;
initial begin
#1000
$finish;
end
endmodule? 运行结果如下:
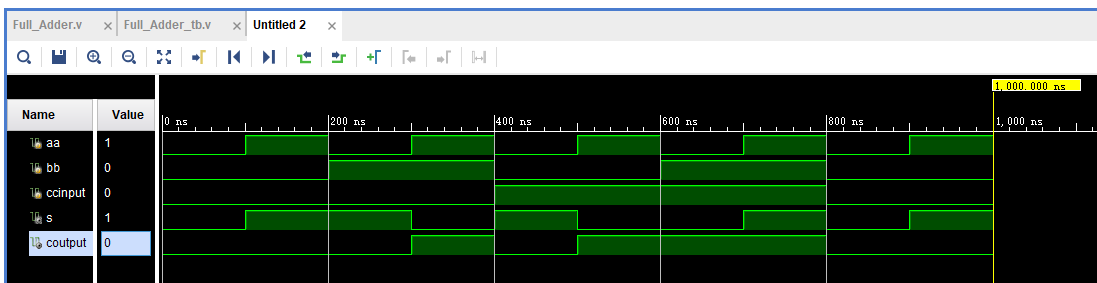
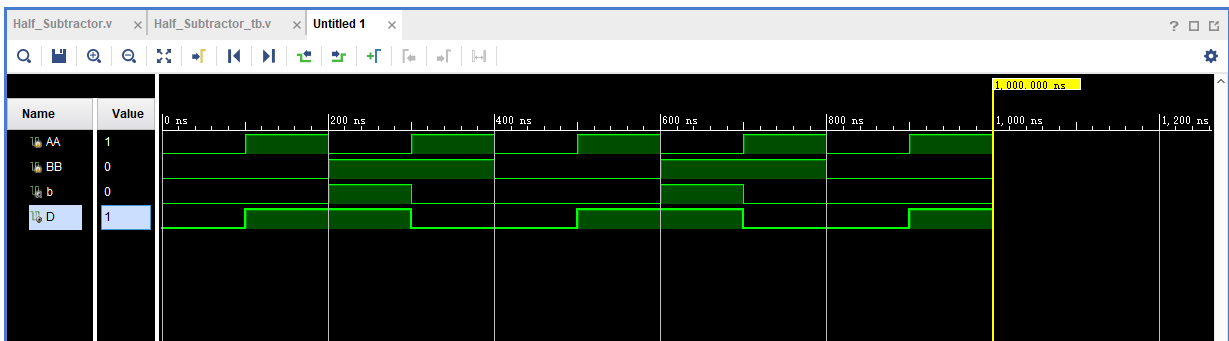
练习3:Half Subtractor
按照下列结构写出 Verilog 代码,得到 Verilog 的 Simulation 结果。
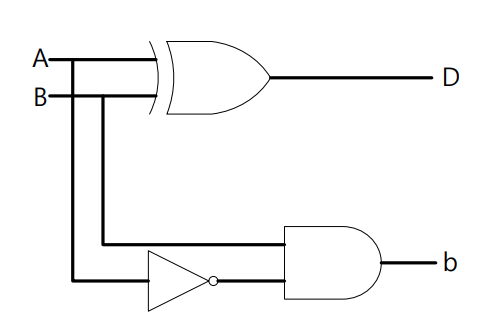
? Design source:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module Half_Subtractor (
input A,B,
output b,D
);
assign D = A ^ B;
assign b = (~A) & B;
endmodule? Testbench:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
/* Half_Subtractor Sim */
module Half_Subtractor_tb;
reg AA, BB;
wire b, D;
Half_Subtractor u_Half_Subtractor(
.A(AA),
.B(BB),
.b(b),
.D(D)
);
initial AA = 1'b0;
initial BB = 1'b0;
always AA = #100 ~AA;
always BB = #200 ~BB;
initial begin
#1000
$finish;
end
endmodule
? 运行结果如下:
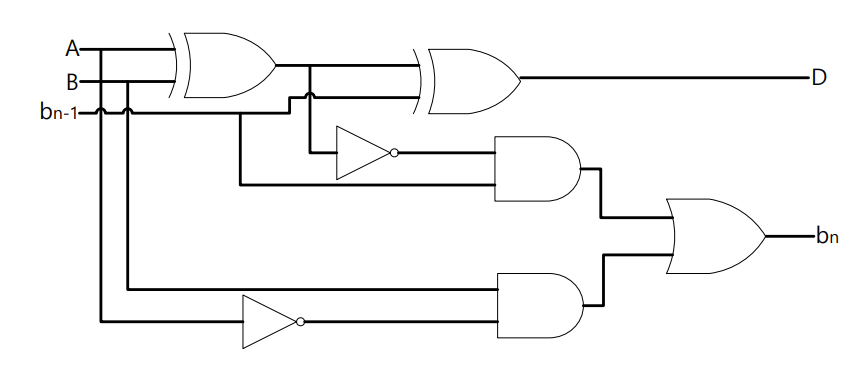
练习4:Full Subtractor
按照下列结构写出 Verilog 代码,得到 Verilog 的 Simulation 结果。
? Design source:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
/* Full_ Subtractor */
module Full_Subtractor (
input a, b, c,
output d, e
);
assign d = (a ^ b) ^ c;
assign e = (~(a ^ b) & c) | (b & ~a);
endmodule
? Testbench:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
/* Full_Subtractor Sim */
module Full_Subtractor_tb;
reg aa, bb, cc;
wire d, e;
Full_Subtractor u_Full_Subtractor(
.a(aa),
.b(bb),
.c(cc),
.d(d),
.e(e)
);
initial aa = 1'b0;
initial bb = 1'b0;
initial cc = 1'b0;
always aa = #100 ~aa;
always bb = #200 ~bb;
always cc = #400 ~cc;
initial begin
#1000
$finish;
end
endmodule? 运行结果如下:
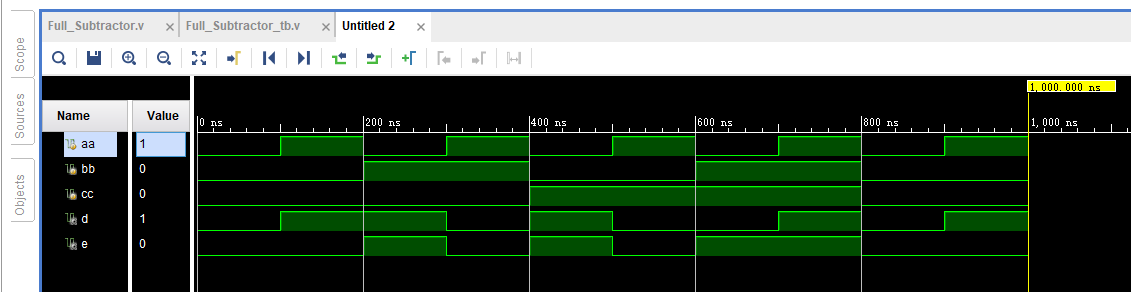
练习4:Code Converter
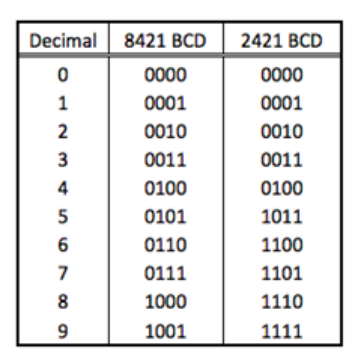 8421(BCD)-2421 Code converter,使用上图表创建真值表,画出卡诺图,使用卡诺图 minimazation 创建布尔函数(SOP form、POS form),分别使用 NAND 和NOR 配置,使用 Verilog 实现 NAND 形式的 8421-2421 converter,使用 FPGA 验证模拟和操作。
8421(BCD)-2421 Code converter,使用上图表创建真值表,画出卡诺图,使用卡诺图 minimazation 创建布尔函数(SOP form、POS form),分别使用 NAND 和NOR 配置,使用 Verilog 实现 NAND 形式的 8421-2421 converter,使用 FPGA 验证模拟和操作。
? Design source:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
/* Code_Converter */
module Code_Converter(
input a, b, c, d,
output e, f, g, h
);
assign e = a || (b && c) || (b && d);
assign f = a || (b && (~d)) || (b && c);
assign g = a || ((~b) && c) || (b && (~c) && d);
assign h = ~(~d);
endmodule? Testbench:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
/* Code_Converter Sim */
module Code_Converter_tb;
reg aa, bb, cc, dd;
wire e, f, g, h;
Code_Converter u_Code_Converter(
.a(aa),
.b(bb),
.c(cc),
.d(dd),
.e(e),
.f(f),
.g(g),
.h(h)
);
initial aa = 1'b0;
initial bb = 1'b0;
initial cc = 1'b0;
initial dd = 1'b0;
always aa = #100 ~aa;
always bb = #200 ~bb;
always cc = #400 ~cc;
always dd = #800 ~dd;
initial begin
#1000
$finish;
end
endmodule
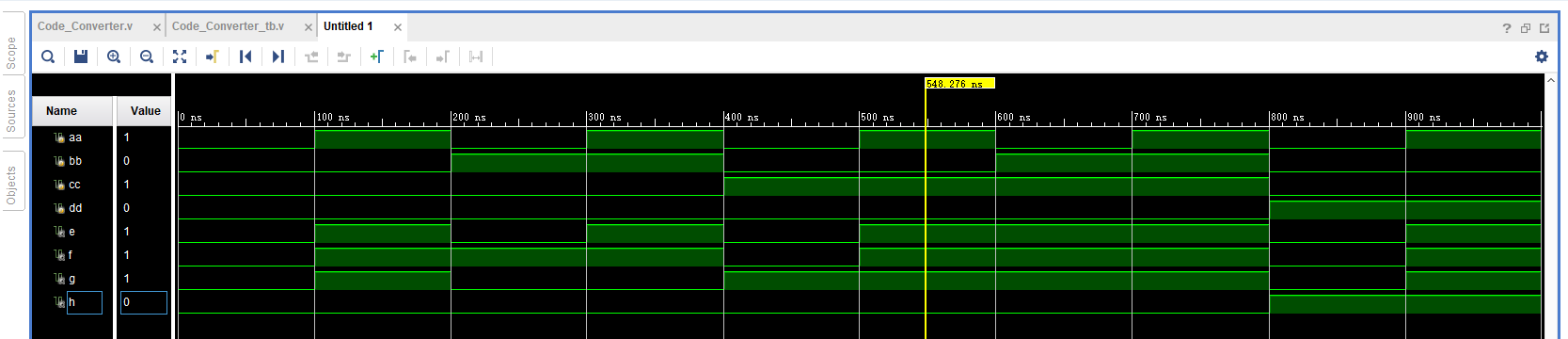
? 运行结果如下:

? [ 笔者 ] 王亦优
? [ 更新 ] 2022.10.5
❌ [ 勘误 ] /* 暂无 */
? [ 声明 ] 由于作者水平有限,本文有错误和不准确之处在所难免,
本人也很想知道这些错误,恳望读者批评指正!| ? 参考资料 Introduction to Logic and Computer Design, Alan Marcovitz, McGrawHill, 2008 Microsoft. MSDN(Microsoft Developer Network)[EB/OL]. []. .文章来源:https://uudwc.com/A/z88e 百度百科[EB/OL]. []. https://baike.baidu.com/.文章来源地址https://uudwc.com/A/z88e |